Which Statement Is True For An Electrochemical Cell

Ever feel like life’s just a bit… static? Like you’re not quite sparking like you could be? Well, hold onto your hats, my friends, because we’re about to dive into the utterly fascinating world of electrochemical cells! And trust me, this isn't some dry textbook lecture. We're talking about the magic behind your phone, the power in a battery, and a whole lot more that makes our modern lives hum along. Pretty cool, right?
So, what exactly is an electrochemical cell? Think of it as a tiny, highly organized chemical party. We’ve got some really special ingredients (chemicals!) that are just itching to get together and… well, react. But not just any old reaction. This is a reaction that’s all about moving little charged particles – we call them electrons – around in a very specific way. And when those electrons start dancing, they create something we can actually use: electricity!
Now, if you've ever seen a science demonstration involving two different metals dipped in a liquid, you’ve basically seen the start of an electrochemical cell. It’s like matchmaking for molecules! One metal is a bit more eager to give up its electrons, and the other is practically begging to receive them. This desire, this chemical potential difference, is the secret sauce that gets the whole show on the road.
So, which statement is true for an electrochemical cell? It’s a question that might sound a bit intimidating, but let’s break it down. At its heart, an electrochemical cell is about a transfer of energy. Specifically, it’s about converting chemical energy into electrical energy. Think of it like a tiny, self-contained power plant, but instead of burning fossil fuels, it's using the inherent "want" of certain chemicals to interact.
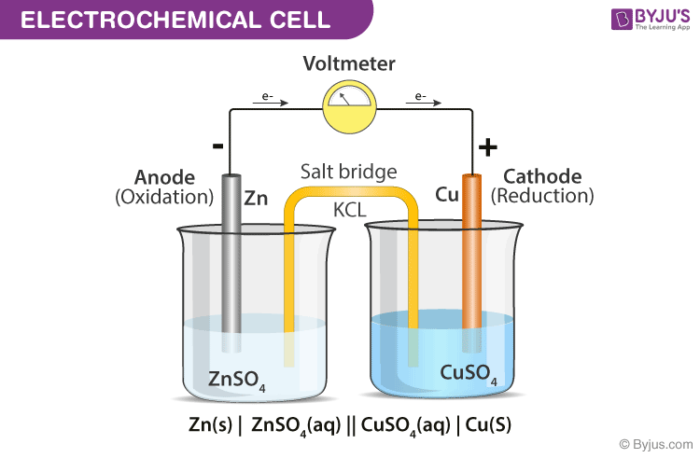
Let’s zoom in a bit. In every electrochemical cell, there are two key players: the anode and the cathode. These aren't just fancy names; they’re crucial roles in our chemical party. At the anode, oxidation happens. Don't let the word scare you! It simply means a substance is losing electrons. It’s like the generous friend at the party, handing out electrons left and right.

And across the way, at the cathode, we have reduction. This is where a substance is gaining those precious electrons. It’s the eager recipient, soaking up all that available energy. So, you’ve got this constant ebb and flow: electrons are being released at one spot and eagerly gobbled up at another. This continuous movement is what creates the electrical current we’re so excited about!
Now, here’s where it gets really fun. For this whole system to work, there needs to be a way for the charged particles (ions, in this case, which are just atoms that have gained or lost electrons and therefore have a charge) to move between the anode and cathode. This is where the salt bridge or a porous membrane comes in. It’s like the diplomatic envoy, ensuring that the overall electrical neutrality is maintained. Without it, the reaction would quickly grind to a halt. It’s all about balance, isn’t it? Even in chemistry!
So, if you’re asked to pick the true statement about an electrochemical cell, you’re looking for something that captures this energy conversion and the flow of electrons. It’s not just about chemicals sitting around; it’s about a process. A dynamic, energy-producing process!
Let’s consider some common misconceptions. Is it true that electrochemical cells consume electricity? Nope! They produce it. That’s their whole raison d'être! Are they only used in tiny, obscure lab experiments? Absolutely not! From the remote control in your hand to the car you might drive (electric ones, that is!), electrochemical cells are powering our world in countless ways. Your smartphone? Huge electrochemical cell inside! That battery that keeps your lights on during a power outage? Yep, you guessed it!

It's also important to remember that not all electrochemical cells are created equal. Some are designed to generate electricity (these are called galvanic cells or voltaic cells – think of your typical battery). Others are designed to use electricity to force a chemical reaction to happen (these are electrolytic cells, used in things like electroplating or refining metals).
But here's the unifying truth: both types involve the interplay of chemical reactions and electrical currents. Both demonstrate the fundamental principle that chemical energy can be converted to electrical energy, or vice versa. It’s a beautiful, elegant dance of electrons and ions.
Think about the sheer ingenuity! Humans figured out how to harness these fundamental forces of nature. It’s like discovering a secret language spoken by atoms, and then learning how to use that language to build amazing things. Doesn't that just make you feel a little bit… powerful?
And the beauty of it is, there’s always more to discover. The world of electrochemistry is vast and full of exciting possibilities. From developing cleaner energy storage solutions to creating new medical technologies, these principles are at the forefront of innovation. It’s a field that’s constantly evolving, constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
So, the next time you flip a switch, charge your phone, or even just marvel at a battery-powered toy, take a moment to appreciate the incredible electrochemical cell working its magic behind the scenes. It’s a testament to the power of chemistry and a reminder that even the smallest interactions can lead to the most remarkable outcomes. Embrace the spark, my friends, and never stop being curious about the electrifying world around you!
