Which Scenario Describes An Interaction Between Two Of Earth's Spheres
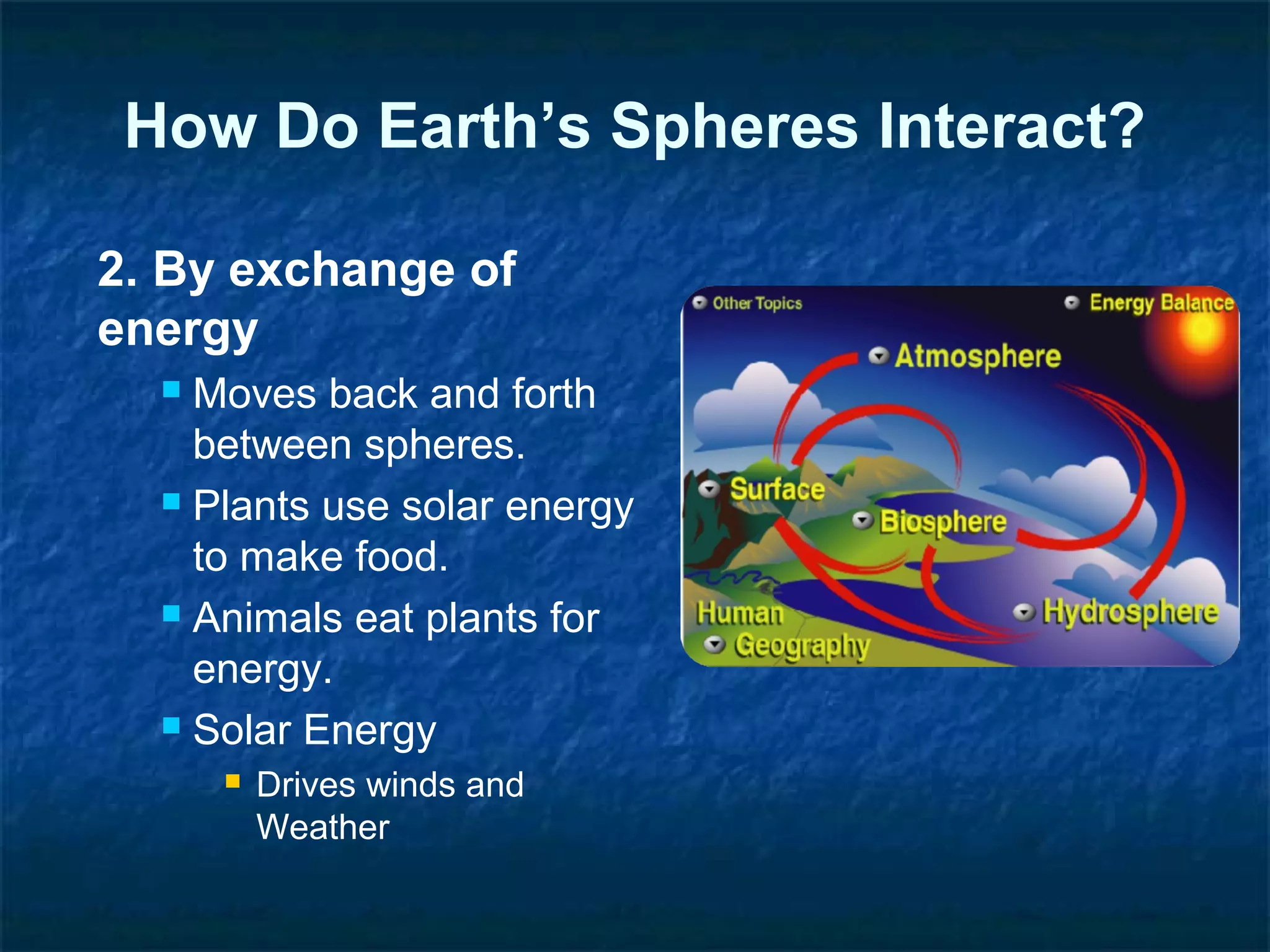
Ever gazed at a majestic mountain range, watched a powerful storm roll in, or felt the gentle kiss of the sun on your skin and wondered about the incredible forces at play? It’s easy to get caught up in our daily routines – grabbing that morning coffee, scrolling through social media, planning our next weekend getaway – and forget that we’re living on a planet that’s a vibrant, interconnected masterpiece. This isn't just a hunk of rock floating in space, folks; it's a dynamic system where different parts constantly interact, creating the world we know and love (and sometimes complain about!).
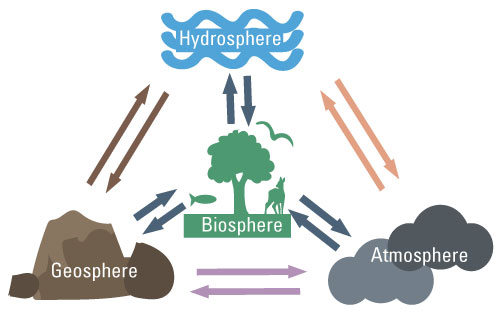
Think of Earth like a super-complex, endlessly fascinating reality show, where different "spheres" are the star contestants, each with their own unique role and personality. We’re talking about the hydrosphere (all the water, from oceans to puddles), the atmosphere (the air we breathe), the geosphere (the solid Earth, from the core to the mountains), and the biosphere (all living things, including us!). And the really cool part? They’re always bumping into each other, collaborating, sometimes clashing, and creating some seriously epic moments. Let's dive into how these Earthly celebrities interact and, more importantly, how these interactions shape our everyday lives.
The Earthly Dance: Spotting Sphere-to-Sphere Shenanigans
So, what does an interaction between two of Earth's spheres actually look like? It’s not as complicated as it sounds, and often, it’s something you’ve witnessed a hundred times without even realizing it. The key is to look for situations where an element from one sphere is directly influencing or being influenced by an element from another.
Scenario 1: The Breath of the Ocean and the Sky
Imagine this: You're on a tropical beach, the sun is beating down, and a gentle breeze is rustling through the palm trees. What's happening here? This is a classic atmosphere-hydrosphere interaction. The warm ocean water (hydrosphere) is evaporating, sending water vapor up into the air (atmosphere). This creates humidity and, on a larger scale, fuels weather patterns like those beautiful, fluffy clouds you see drifting by. Think of those stunning sunset photos you love – the vibrant colors are often enhanced by atmospheric particles interacting with sunlight, a direct consequence of atmospheric processes often initiated by evaporation from the hydrosphere.
Fun Fact: Did you know that the vast majority of Earth's water is saltwater, locked away in the oceans? Only a tiny fraction is freshwater, which is why understanding these atmospheric-hydrospheric exchanges is so crucial for our planet's water cycle. It's like Earth's giant, free humidifier and air conditioner, all rolled into one!
Practical Tip: Next time you're near a large body of water, take a deep breath. You’re literally inhaling moisture that has cycled through the atmosphere thanks to the hydrosphere. This is why coastal areas often have a refreshing, clean air quality. Try a mindful breathing exercise by the sea or a lake – it's a mini-retreat powered by Earth’s spheres!
Scenario 2: Mountains Meeting the Wind
Picture yourself hiking in the mountains. You're surrounded by towering peaks, and the wind is whipping around you. This is a prime example of geosphere-atmosphere interaction. The solid rock and earth that make up the mountains (geosphere) are directly interacting with the moving air (atmosphere). The shape and height of mountains can influence wind patterns, creating localized winds or even affecting regional weather. Ever noticed how windy it gets at higher elevations? That's the atmosphere being redirected by the geosphere.

Cultural Reference: Think of myths and legends involving mountain spirits or gods. These stories often reflect a deep, ancient understanding of the power and influence of these landforms. The wind howling through the peaks could easily have been interpreted as the breath of a mighty deity in ancient times. Think of the Greek gods on Mount Olympus – the atmosphere swirling around them was as much a part of their domain as the rocky terrain.
Fun Fact: Mountain ranges can actually influence rainfall! When moist air from the ocean encounters a mountain range, it’s forced upward. As it rises, it cools, and the water vapor condenses to form clouds and rain on the windward side of the mountain. The leeward side, often in the "rain shadow," can be much drier. This is why places like the Pacific Northwest have lush forests, while the deserts of Nevada are just a few hundred miles away!
Practical Tip: If you’re planning a hike, always check the weather forecast, especially for mountainous areas. The atmosphere can change rapidly due to interactions with the geosphere, and a sunny day can quickly turn into a windy, rainy ordeal. Dressing in layers is key to staying comfortable and safe – a little respect for the elements goes a long way.
Scenario 3: The Living Forest and the Earth Below
Close your eyes and imagine a lush, ancient forest. The trees are towering, their roots digging deep into the soil. This is a beautiful demonstration of biosphere-geosphere interaction. The plants and trees (biosphere) are deeply intertwined with the soil and rock beneath them (geosphere). Tree roots help to break down rocks over time, creating soil, and they also help to hold the soil in place, preventing erosion. The nutrients in the soil are essential for plant growth, and when plants decay, they add organic matter back into the soil, enriching it for future generations of life.
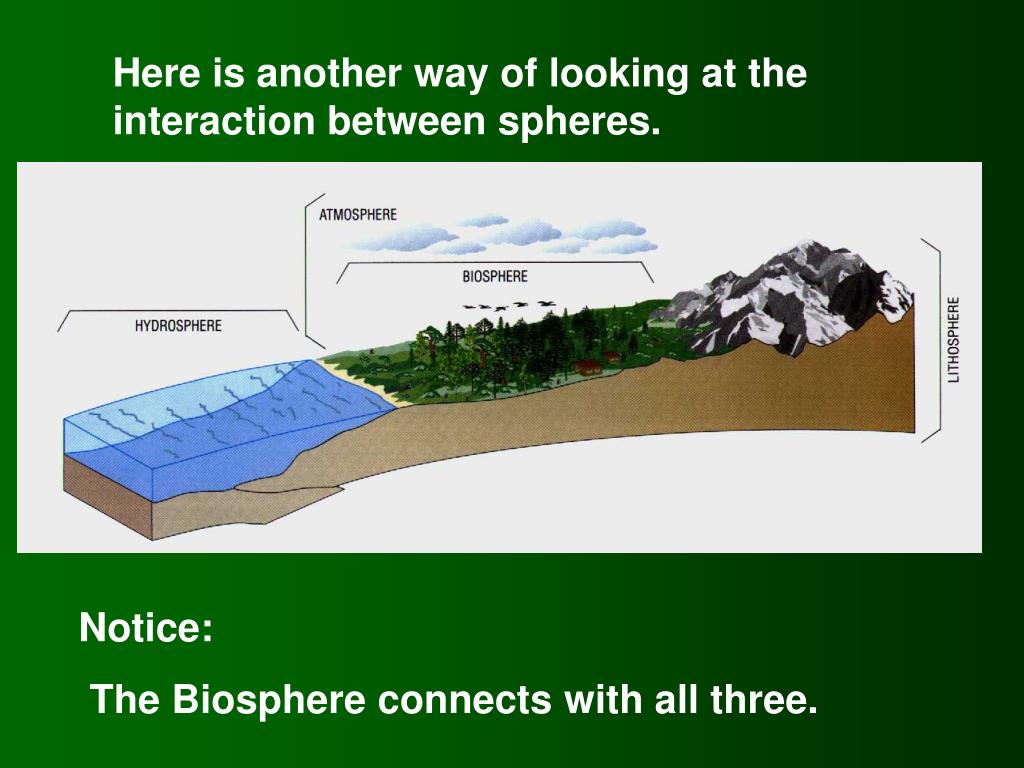
Cultural Reference: Many indigenous cultures have profound spiritual connections to the land and its ecosystems. Practices like sustainable agriculture or traditional forest management often stem from an intuitive understanding of these biosphere-geosphere relationships. The concept of "Mother Earth" is a testament to this deep respect for the interconnectedness of life and the ground that sustains it.
Fun Fact: Soil isn't just dirt! It’s a complex mixture of minerals, organic matter, water, and air, teeming with life. A single teaspoon of healthy soil can contain billions of microorganisms, all playing a vital role in the ecosystem. These tiny helpers are a crucial part of the biosphere's connection to the geosphere.
Practical Tip: If you have a garden or even just a potted plant, you're engaging in biosphere-geosphere interaction! Using good quality compost (organic matter from the biosphere) will enrich your soil (geosphere), leading to healthier plants. It’s a small-scale model of a global process. Consider starting a small compost bin – it's a fantastic way to reduce waste and give back to the Earth.
Scenario 4: The Hungry Organism and its Environment
Let’s think about something a bit more direct. Imagine a deer (biosphere) nibbling on grass (biosphere) that’s growing in the soil (geosphere) under the open sky (atmosphere). This scenario involves multiple sphere interactions, but let's focus on the deer and the soil. The deer, as part of the biosphere, directly interacts with the geosphere by walking on it, compacting it, and contributing to its nutrient cycle through waste. The grass it eats is also a product of the geosphere (soil nutrients) and the atmosphere (sunlight and CO2 for photosynthesis).

Cultural Reference: The concept of the food chain, a cornerstone of biology, is essentially a series of biosphere-biosphere and biosphere-geosphere interactions. From the smallest insect to the largest predator, all life is connected through these exchanges. Think of cave paintings depicting hunts – they're early visual records of these vital interactions.
Fun Fact: The carbon cycle, a fundamental process for life on Earth, involves continuous exchange between the biosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and geosphere. Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, incorporate it into their tissues (biosphere), and when they die, this carbon can be stored in the soil (geosphere) or oceans (hydrosphere).
Practical Tip: When you’re out for a walk in nature, take a moment to appreciate the life around you and how it’s connected to the ground beneath your feet. Even noticing a worm tilling the soil or a bird building its nest is observing these essential interactions. It’s a great way to foster a sense of wonder and connection to the natural world.
Scenario 5: The Cracking Earth and the Water's Influence
This one sounds a bit more dramatic, and it can be! Think about how water can affect rock over long periods. Water seeping into cracks in rocks (geosphere), then freezing and expanding, can cause the rock to break apart (weathering). This is a powerful hydrosphere-geosphere interaction. Over geological timescales, this process shapes landscapes, creating canyons, valleys, and the very ground we walk on. Think of the Grand Canyon – a monumental testament to the erosive power of water.
Cultural Reference: Many ancient civilizations built their settlements near water sources, recognizing its power for life and its ability to shape the land. The construction of aqueducts, dams, and irrigation systems are all testaments to humanity’s understanding and manipulation of these hydrosphere-geosphere interactions for survival and prosperity.
Fun Fact: Freeze-thaw cycles are a major driver of rock weathering. In colder climates, this process can be particularly intense. It’s like nature’s own little demolition crew, slowly but surely breaking down even the hardest rocks. This is also why potholes form on roads – water gets into tiny cracks, freezes, expands, and weakens the asphalt.
Practical Tip: When you see water collecting in cracks in sidewalks or driveways, you’re witnessing the very beginnings of this process. While on a small scale, it’s a reminder of the constant, subtle forces shaping our planet. It also highlights the importance of proper drainage around your home – a little bit of prevention goes a long way in protecting your property from the persistent power of water.
Bringing It All Home
These interactions between Earth's spheres aren't just abstract scientific concepts; they are the very fabric of our existence. The air we breathe is shaped by the oceans and landforms. The food we eat is a product of the soil, the sun, and the rain. The landscapes that inspire us are sculpted by geological forces and the relentless work of water and wind.
Reflection: This morning, as I brewed my coffee, I thought about where those beans came from – likely grown in rich soil, watered by rain, and transported across continents. That simple act, connecting me to the biosphere, the geosphere, and the hydrosphere, is a daily reminder of the vast, invisible network that sustains us. Every sip was a little taste of Earth’s magnificent symphony. So next time you're out and about, whether it’s a walk in the park, a drive through the countryside, or just looking out your window, take a moment to notice the subtle (and sometimes not-so-subtle) interactions happening all around you. It’s a beautiful, ongoing conversation between the spheres, and we’re all invited to be a part of it.
