Which Quantity Represents The Number Of Protons In An Atom
..jpg)
Ever wonder what makes a carbon atom a carbon atom, and not, say, an oxygen atom? It’s a question that might seem a bit niche, but trust us, it’s the secret handshake of the universe, the fundamental blueprint that dictates everything from the sparkle in a diamond to the very air you breathe! Understanding this core concept unlocks a fascinating world of chemistry and physics, and it’s surprisingly accessible. Think of it like learning the secret password to a whole new dimension of understanding how the world around you works. It’s not just for scientists; it’s for anyone who’s ever looked at a star and wondered, or been amazed by the sheer variety of materials we have at our fingertips. This fundamental knowledge is the key to appreciating the intricate dance of matter that makes up our reality.
The purpose of diving into this topic is to demystify the building blocks of everything. At its heart, it’s about identity. Every element on the periodic table, from the lightest hydrogen to the heaviest synthetic ones, has a unique identifier. This identifier isn't a complex code or a magical incantation; it's a simple number that tells us precisely what that atom is made of at its core. Knowing this number is like having a universal translator for the atomic world. It allows us to predict how atoms will interact, what kind of compounds they will form, and ultimately, why certain substances have the properties they do.
The benefits of grasping this concept are far-reaching. For starters, it makes learning chemistry a whole lot easier. Instead of memorizing endless facts about each element, you can understand the underlying principle that governs their behavior. This foundational knowledge is crucial for anyone pursuing careers in science, technology, engineering, or medicine. But even if you're just curious about the world, it enriches your understanding. Imagine knowing that the difference between your trusty iron frying pan and a super-conductive material is simply a change in this fundamental atomic characteristic! It’s empowering, it's educational, and frankly, it’s pretty cool.
So, what is this magical number that defines an atom? drumroll please... it’s the atomic number! Yes, it’s that simple. The atomic number is the one true characteristic that sets each element apart. It’s not the weight, it’s not the size; it’s the count of a specific subatomic particle residing within the atom's nucleus. This particle is the proton. Think of protons as the atom's VIP guests, always present and always defining its identity. They are positively charged little guys, and their number is non-negotiable for a given element.
Every atom of a particular element will have the exact same number of protons. For instance, every single atom of gold has 79 protons. Not 78, not 80, but precisely 79. This is why we call it gold. If you were to somehow change the number of protons in a gold atom, it wouldn't be gold anymore; it would be a different element altogether! This is the fundamental principle that governs the periodic table, that grand chart that organizes all the known elements. The elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, a testament to the importance of this single, defining quantity.
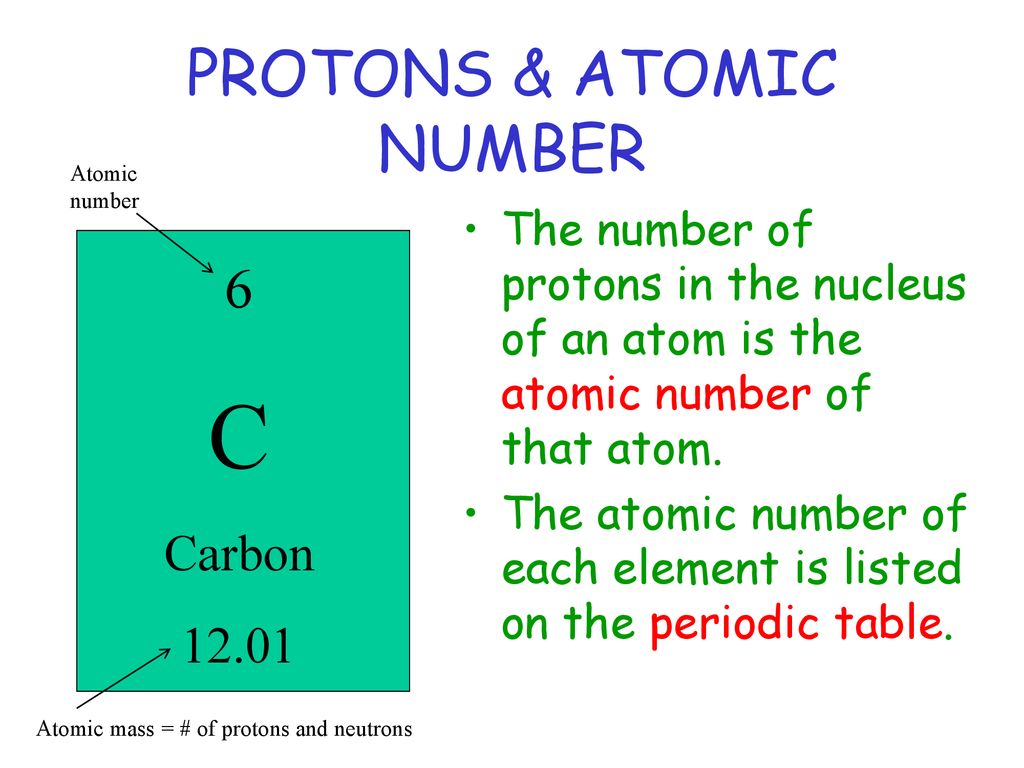
Let's take a quick look at some familiar elements. Hydrogen, the simplest and most abundant element in the universe, has an atomic number of 1. This means every hydrogen atom has just one solitary proton in its nucleus. Helium, the gas that makes balloons float and gives cartoon voices that funny squeak, has an atomic number of 2. So, it has two protons. Oxygen, essential for our breathing, clocks in with an atomic number of 8, meaning it has eight protons. See the pattern? It's a direct one-to-one correlation: atomic number equals the number of protons.
This concept is so vital because protons are the anchors of an atom. They reside in the atom's central core, the nucleus, along with another type of particle called neutrons. While neutrons contribute to the atom's mass, they don't affect its identity. Protons, on the other hand, are the identity keepers. They carry a positive electrical charge, and this charge is what attracts the negatively charged electrons that orbit the nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons perfectly balances the number of protons, making the overall charge zero.

The number of protons is the bedrock of an element's chemical properties. It dictates how readily an atom will bond with other atoms, the types of molecules it will form, and its reactivity. For example, elements with fewer protons, like alkali metals (sodium, potassium), tend to be very reactive and readily lose an electron. Elements with more protons, like noble gases (neon, argon), have a full outer shell of electrons and are generally unreactive. All of this behavior stems back to that one simple number – the number of protons.
So, the next time you hear about an element, whether it’s the carbon in your body, the silicon in your computer, or the iron in your blood, remember that its fundamental identity, its very essence, is determined by the number of protons it possesses. This single quantity, the atomic number, is the universe's way of labeling its fundamental ingredients. It’s a beautiful, elegant system that underlies the complexity and diversity of the material world. It’s a cornerstone of our understanding of matter, and a concept that, once grasped, opens up a whole new appreciation for the science all around us.
The number of protons in an atom's nucleus is known as its atomic number. This number is the defining characteristic of an element and determines its place on the periodic table.
This isn't just a piece of trivia; it's the key that unlocks the secrets of chemistry. Understanding the atomic number and its relationship to the number of protons allows us to decipher the behavior of elements and predict how they will interact. It's like learning the alphabet before you can read a book. The atomic number is the alphabet of elements, and protons are the letters that spell out their identity.
