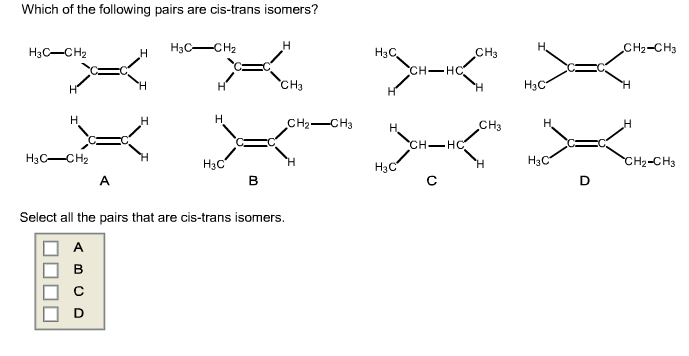
Which Of The Following Pairs Of Compounds Are Cis-trans Isomers
Hey there, fellow curious minds! Ever find yourself staring at a puzzle, a complex recipe, or even just trying to arrange your furniture just right? There's a special kind of satisfaction in figuring out how things fit together, isn't there? Well, get ready to flex those mental muscles because we're diving into a fascinating world that’s all about how molecules can look the same but be… well, a little different. Think of it as the molecular equivalent of a really good optical illusion, or perhaps a challenging game of “spot the difference” for chemists!
This might sound a bit technical, but understanding concepts like cis-trans isomerism actually has some surprisingly practical applications in our everyday lives. You see, the specific arrangement of atoms in a molecule can dramatically affect its properties. For instance, in the world of fats and oils, the difference between a cis and a trans fat can be the difference between something your body processes easily and something that can be a bit more challenging. Understanding these subtle differences helps us make informed choices about the food we eat and the products we use, from pharmaceuticals to plastics. It's about appreciating the elegance of molecular structure and how it dictates function.
You might have encountered examples without even realizing it! Think about the smell of a rose versus the smell of a skunk – sometimes, a tiny shift in atomic arrangement is responsible for a huge difference in scent. In pharmaceuticals, the way a drug molecule is shaped can determine if it fits perfectly into its target site in the body, like a key in a lock, or if it’s completely ineffective. Even the way your phone screen displays images relies on molecules that have specific structural orientations. So, while you might not be drawing Lewis structures every day, the principles of isomerism are at play all around you!
Now, how do we get better at spotting these cis-trans pairs? It’s all about looking for a specific structural feature: a double bond connecting two carbon atoms (or sometimes another atom like nitrogen). For cis-trans isomerism to exist, each of those double-bonded carbon atoms must be attached to two different groups. Once you've identified a double bond with the right setup, the "cis" isomer has these two different groups on the same side of the double bond, while the "trans" isomer has them on opposite sides. Think of it as two people facing each other across a fence (trans) versus two people standing side-by-side looking in the same direction (cis). Practice is key! Try drawing out some simple examples yourself. Start with molecules like butene and then move to slightly more complex ones. Visualizing these structures, perhaps even using molecular modeling kits if you’re feeling adventurous, can be incredibly helpful. And don't be afraid to consult diagrams and examples online – there are tons of resources available to help you master this skill. It’s a fun mental workout that sharpens your observation skills and gives you a deeper appreciation for the intricate world of chemistry!
