Which Of The Following Are Geometric Sequences Apex
Ever find yourself staring at patterns and wondering, "Is there a hidden rule here?" That's the exact feeling that drew me into the fascinating world of geometric sequences. It’s like discovering a secret handshake in nature or a clever trick in a game. Understanding these patterns isn't just about acing a math test; it's about unlocking a way of seeing the world that's both elegant and useful.
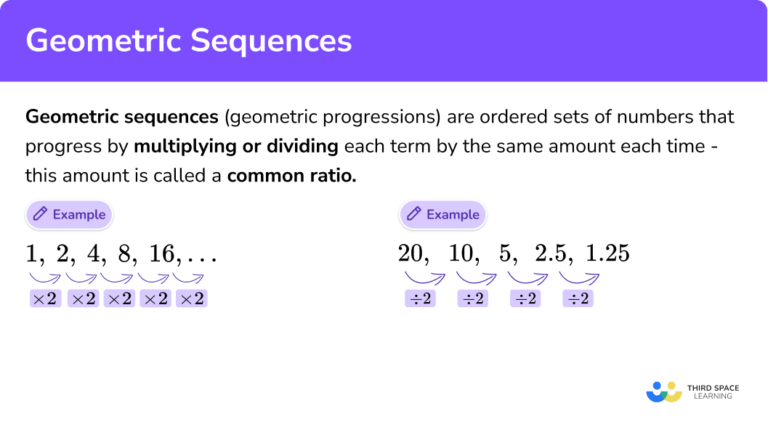
So, what exactly are we talking about? A geometric sequence is a series of numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous one by a fixed, non-zero number called the common ratio. Think of it as a multiplier that keeps the pattern going. Unlike arithmetic sequences, where you add a constant value, geometric sequences involve growth or decay that can be incredibly powerful.
The purpose of understanding geometric sequences is pretty broad. For starters, they help us model situations involving repeated multiplication. This can range from financial calculations to biological growth. The benefits are tangible: you can better predict how something will change over time, whether it's the value of an investment or the spread of a rumor (though hopefully a good one!). In education, they're a fundamental building block for understanding more complex mathematical concepts like exponential functions, which are everywhere.
Where do we see these sequences pop up? In finance, for instance, compound interest is a classic example. Your money grows not just on the initial deposit but also on the accumulated interest – a geometric progression in action! Think about a savings account where interest is calculated annually. If you have $1000 and earn 5% interest each year, your money becomes $1050, then $1102.50, and so on. That 1.05 multiplier is your common ratio. In biology, you might see populations of bacteria or viruses growing geometrically under ideal conditions, doubling at regular intervals. Even in everyday life, you might notice it with things like how many times you can fold a piece of paper (though this has physical limits!) or the way a bouncing ball loses a consistent percentage of its height with each bounce.
Curious to explore this yourself? It’s easier than you might think! Start by looking for patterns in sequences of numbers. If you see a consistent multiplier, you're likely on the trail of a geometric sequence. For example, the sequence 2, 6, 18, 54... has a common ratio of 3 (6/2 = 3, 18/6 = 3, and so on). You can even try creating your own! Pick a starting number and a common ratio, then multiply your way to a new sequence. Maybe start with 5 and a ratio of 2: 5, 10, 20, 40... See what kind of patterns emerge. You might be surprised by how much mathematical beauty you can uncover with just a little curiosity and a simple multiplier.
