Which Is Not True According To Mendel's Law Of Segregation
Ever wondered why you might have your dad's curly hair but your mom's blue eyes? Or why your pet hamster seems to have a mix of traits from its parents? These are all fascinating questions rooted in the fundamental principles of heredity, and at the heart of it all lies the brilliant work of Gregor Mendel, often hailed as the "father of genetics." Learning about Mendel's laws isn't just for science buffs; it's like unlocking a secret code that explains so much about the living world around us, including ourselves! It’s a journey into understanding the very essence of what makes us, us, and what makes a rose a rose, or a cat a cat.
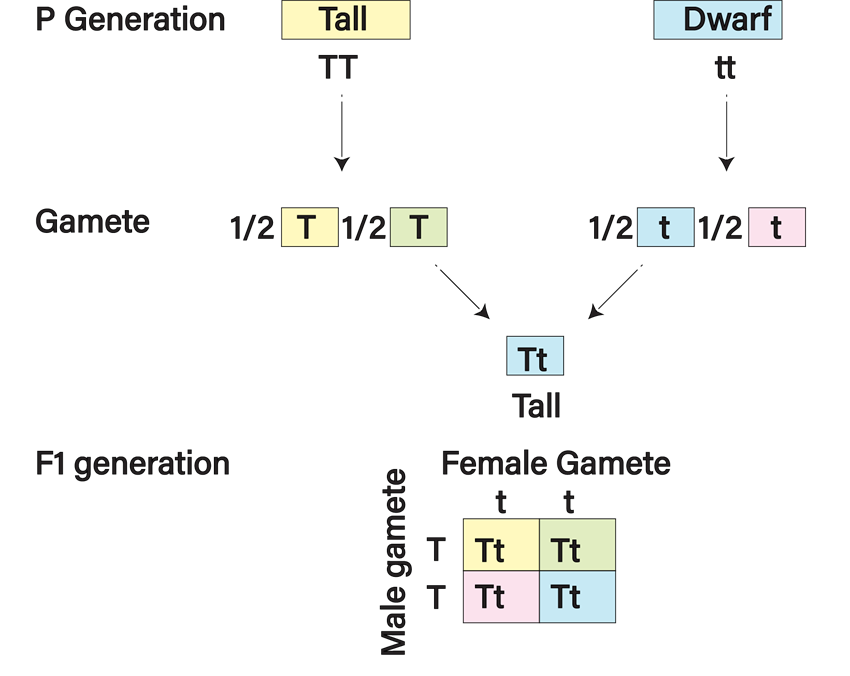
Mendel's Law of Segregation is a cornerstone of genetics, and understanding it helps us grasp how traits are passed down from one generation to the next. Its core purpose is to explain the behavior of alleles – the different versions of a gene. According to this law, for any given trait, an individual inherits two alleles, one from each parent. During the formation of reproductive cells (sperm and eggs), these two alleles separate or segregate, so that each reproductive cell receives only one allele. This simple yet profound idea is the reason why siblings, even from the same parents, can have different combinations of traits. It's not about a blend; it's about distinct units of inheritance that sort themselves out.
The benefits of understanding Mendel's Law of Segregation are far-reaching. In education, it forms the basis for teaching genetics, helping students understand inheritance patterns in biology classes. Beyond the classroom, this knowledge has incredible practical applications. Think about agriculture: farmers use these principles to selectively breed crops and livestock for desirable traits like disease resistance or higher yield. In medicine, understanding segregation helps in predicting the likelihood of inheriting certain genetic conditions. Even in choosing a pet, knowing about dominant and recessive traits (which are closely related to segregation) can influence decisions about breeding or understanding potential health issues.
So, how can you explore this fascinating concept without needing a lab coat? It's surprisingly easy! Start by observing the traits within your own family. Do you notice any patterns? Perhaps a certain eye color skips a generation or appears more frequently on one side of the family. You can also look at plants in your garden or even at pictures of different dog breeds. For example, think about pea plants, just like Mendel did! If you have access to different colored flowers or different shaped leaves, you can start to imagine how those traits might be inherited. Another fun way is to look at simplified Punnett squares, which are diagrams that help visualize the possible combinations of alleles. There are many educational websites and videos that explain these concepts with clear examples, often using simple analogies that make the science feel accessible and even entertaining.
The beauty of Mendel's Law of Segregation lies in its elegant simplicity and its immense explanatory power. It's a fundamental piece of the puzzle that helps us understand the incredible diversity of life and the continuity of traits across generations. So next time you see a trait that seems to come from one parent but not the other, remember Mendel and his pea plants – you're witnessing the principles of segregation in action!
