Which Graph Represents The Solution Set Of The Inequality
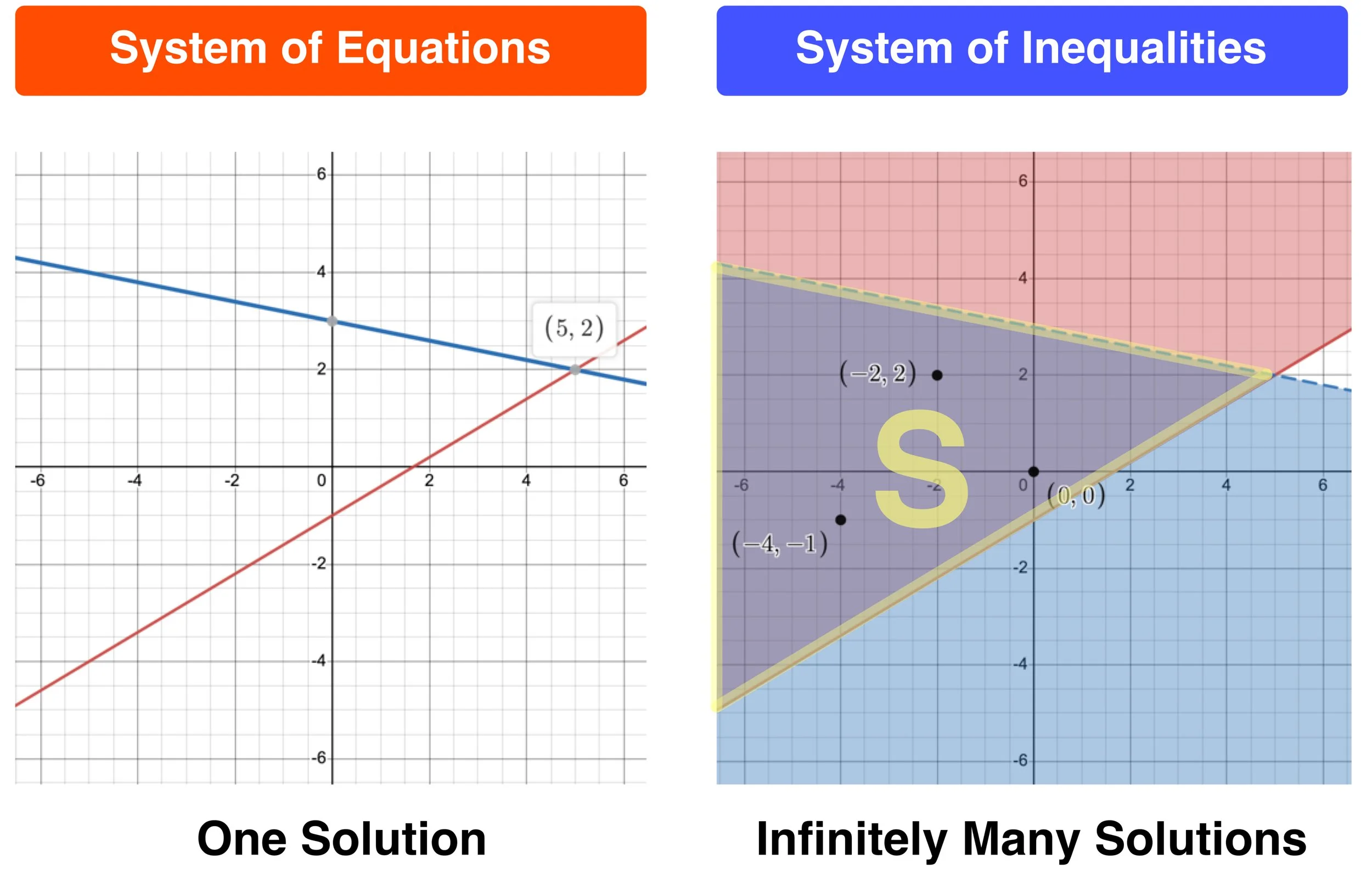
Ever stare at a math problem that looks like it's speaking a secret language? You know, the one with the little squiggly lines and arrows? Don't worry, you're not alone! Today, we're going to tackle something that sounds a bit scary but is actually super useful, like figuring out the perfect amount of ice cream for your cone – we're talking about "Which Graph Represents The Solution Set Of The Inequality".
Think of an inequality like this: it’s a rule. It tells you what's allowed and what's not. For instance, imagine your parents tell you, "You can have more than two cookies, but not five or more." This is an inequality in disguise! You can have 3 or 4 cookies, but definitely not 1, 2, or 5, 6, 7, and so on. It sets a boundary, a limit, a range of possibilities.
Now, where do graphs come in? Graphs are like a picture book for these rules. Instead of just saying "more than two, less than five," a graph can show you all the numbers that work. It's like drawing a line on a map to show all the places you're allowed to go for a fun afternoon. No more guessing games!
So, Why Should We Even Care?
This might seem like something only your math teacher needs to worry about, but trust me, it pops up in our everyday lives more than you think!
Let's say you're planning a road trip. Your budget for gas is, let's be generous, up to $100. That's an inequality! You can spend $99.50, or $50, or even $10. But you can't spend $101. A graph could visually show you all the possible gas amounts within your budget. It helps you stay on track and avoid that dreaded "uh oh, we're out of money" moment.
Or, think about baking. A recipe might say you need at least 3 cups of flour. This means you can use 3 cups, 3.5 cups, or even 4 cups if you're feeling adventurous. But you definitely can't use 2.5 cups! Using a graph to understand this inequality can help you avoid a flat, sad cake and ensure a fluffy, delicious success.

It's all about setting boundaries and understanding the possibilities. Whether it's about money, ingredients, or even how much time you have to binge-watch your favorite show (less than 3 hours, sadly!), inequalities and their graphical representations help us make sense of the world around us.
Decoding the Mystery: What Does the Graph Tell Us?
When we see a graph representing an inequality, it's usually on a number line. Imagine a long, straight road with numbers all along it. The inequality tells us which parts of that road are "allowed" or "good."
Let's take our cookie example: "more than two cookies, but not five or more." On a number line, we'd look for the number 2 and the number 5. If the rule is "more than two," we'd shade in all the numbers after 2. If the rule is "not five or more," we'd stop shading before we get to 5. It’s like drawing a bright, happy line showing all the cookie counts that make you smile.

Sometimes, you'll see a little circle on the graph. This circle can be open or closed. Think of it like a gate. An open circle means that the number right at that spot is not included in the solution. So, if your rule is "more than 2 cookies," the circle at 2 would be open because you can't have exactly 2 cookies; you need more.
A closed circle, on the other hand, means that the number at that spot is included. If the rule was "two or more cookies," the circle at 2 would be closed because 2 is a perfectly acceptable number of cookies!
Then, there's the shading. The shaded part of the number line shows all the numbers that satisfy the inequality – all the delicious possibilities! If you shade to the right of a number, it usually means "greater than" or "greater than or equal to." If you shade to the left, it means "less than" or "less than or equal to." It's like painting the "happy path" on our number road.
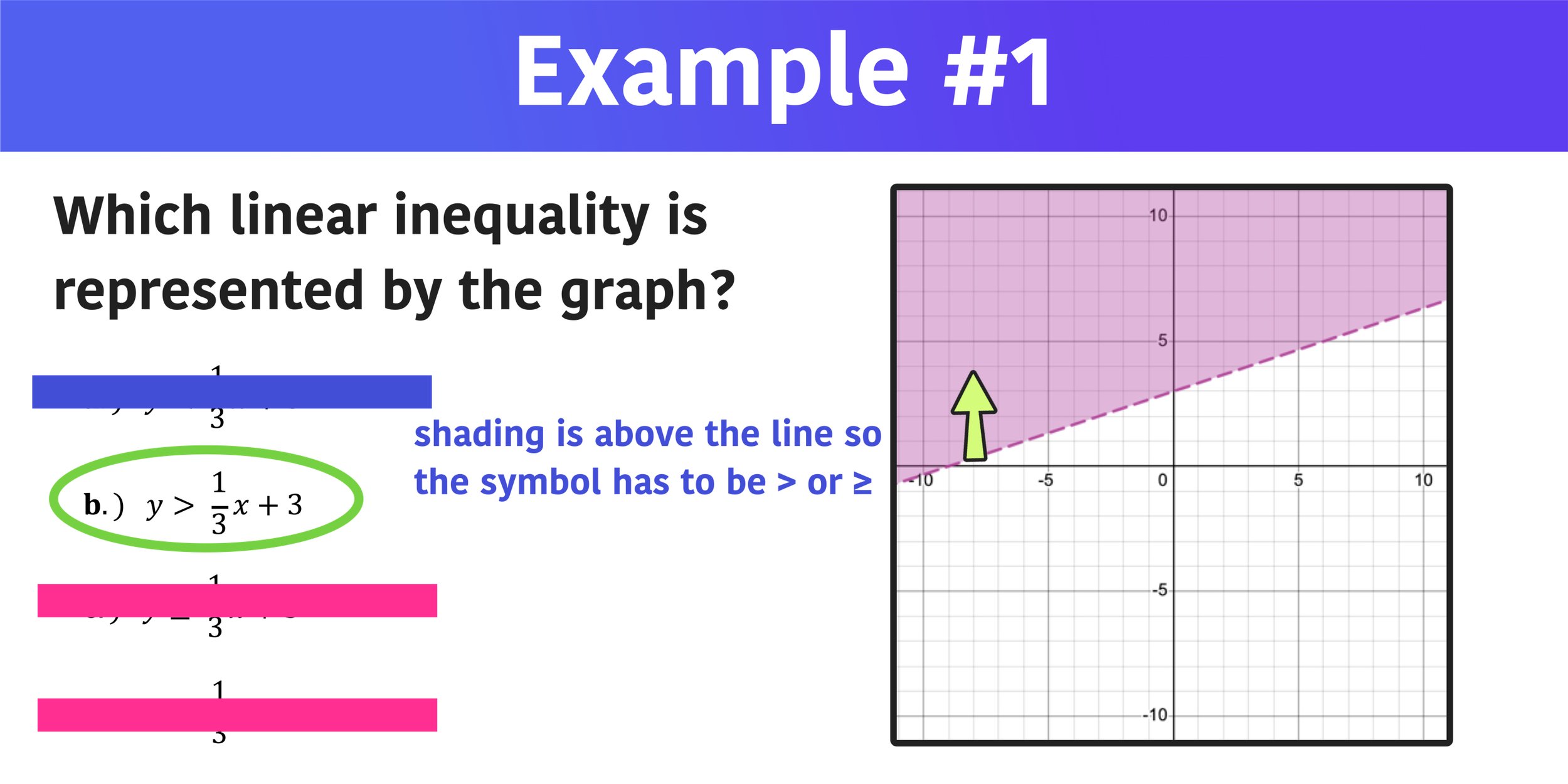
Putting It All Together: Finding the Right Graph
So, when you're faced with a question like "Which graph represents the solution set of the inequality?", here's your secret decoder ring:
- Identify the Numbers: Look at the numbers in your inequality. These are your stopping and starting points.
- Check the Symbols: See those little "<", ">", "≤", "≥" signs? They're the key! '<' and '>' mean "not included" (open circle). '≤' and '≥' mean "included" (closed circle).
- Follow the Shading: Does the shaded area go to the left or right? This tells you if you're looking for numbers smaller or larger than your boundary numbers.
Let's imagine a scenario. Your friend tells you, "I'll meet you at the park, but only if it's after 3 PM and before 5 PM."
On a number line of time, you'd look at 3 PM and 5 PM. Since it's "after 3 PM" (not including 3 PM exactly), you'd have an open circle at 3. Since it's "before 5 PM" (not including 5 PM exactly), you'd have an open circle at 5. And the "only if" part means you're interested in the time between 3 and 5. So, you'd shade the line segment connecting those two open circles.
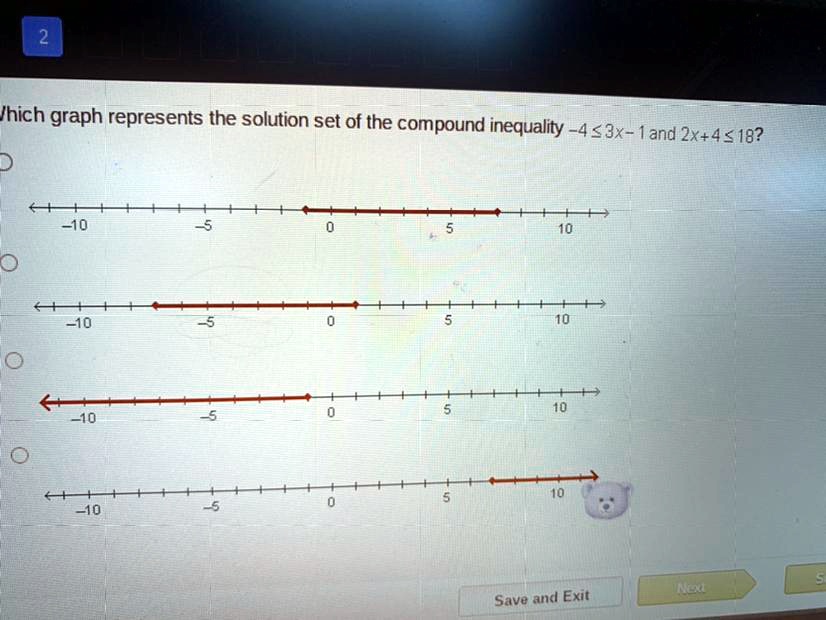
It's like drawing a little happy sandwich of time where you get to meet your friend! This is the solution set – all the possible meeting times.
Understanding these graphs isn't just about passing a math test. It's about having a clear picture of what's possible. It's about making informed decisions, whether it's managing your money, planning your day, or even deciding how many cookies you can really have without getting a tummy ache!
So next time you see a graph with a shaded line and some circles, don't let it intimidate you. Think of it as a friendly guide, showing you all the awesome possibilities. It's a little bit of math magic that makes the everyday world a little easier to navigate, one solution set at a time!
