What Property Of The Phospholipid Bilayer Allows Proteins
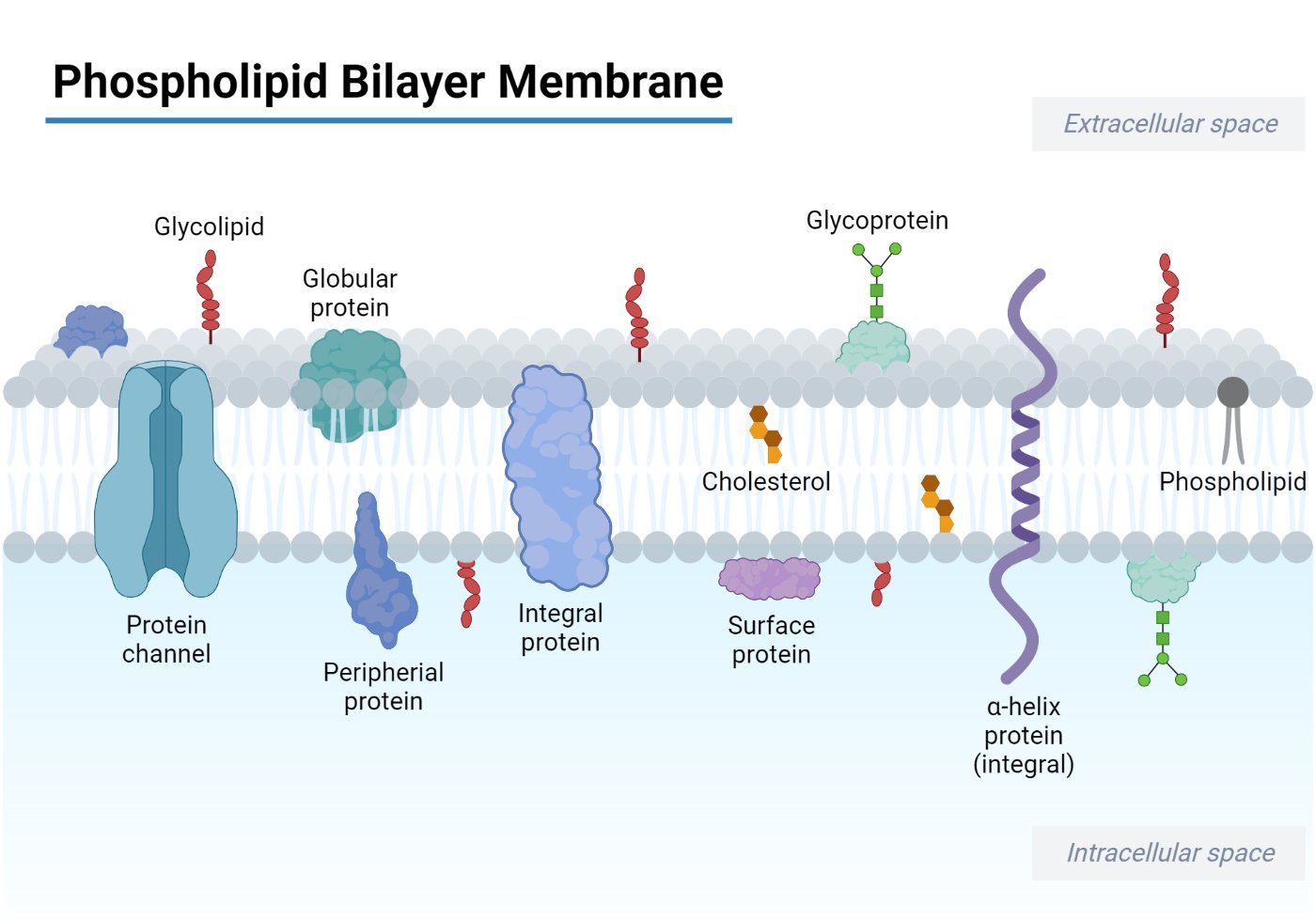
Ever marvel at how your smartphone seamlessly connects you to the world, or how your favorite recipe transforms simple ingredients into culinary masterpieces? These everyday wonders, and so much more, owe a debt to a fundamental biological concept: the phospholipid bilayer. While it might sound like something out of a science textbook, understanding its unique property is key to appreciating how life's intricate machinery works, right down to the very cells that make us tick!
So, what's so special about this phospholipid bilayer that allows proteins – the workhorses of our cells – to do their jobs? The secret lies in its amphipathic nature. Imagine a molecule with a "head" that loves water and a "tail" that actively avoids it. That's our phospholipid! When these molecules gather in an aqueous environment, like inside and outside our cells, they naturally arrange themselves into a double layer. The water-loving heads face outwards, interacting with the watery surroundings, while the water-fearing tails huddle together in the middle, creating a hydrophobic core. This clever arrangement forms a stable barrier.
This barrier isn't just a wall; it's a highly selective gatekeeper! The hydrophobic core of the bilayer is largely impermeable to most water-soluble molecules, effectively controlling what enters and leaves the cell. And this is where proteins come in. Because proteins are often large or charged, they can't just wander through this fatty middle ground. Instead, they are strategically embedded within or associated with the phospholipid bilayer. This embedding allows them to perform a multitude of vital functions:
Proteins acting as channels can create specific passageways for particular ions or molecules to cross the barrier, like microscopic turnstiles. Others act as pumps, actively transporting substances against their concentration gradients, requiring energy. Receptor proteins on the surface of the cell can bind to external signals, triggering intracellular responses – think of them as the cell's communication antennae. Enzymes embedded within the membrane can catalyze reactions right at the cell's edge, facilitating essential metabolic processes. Without the phospholipid bilayer's ability to anchor and orient these diverse proteins, cells simply wouldn't be able to function.
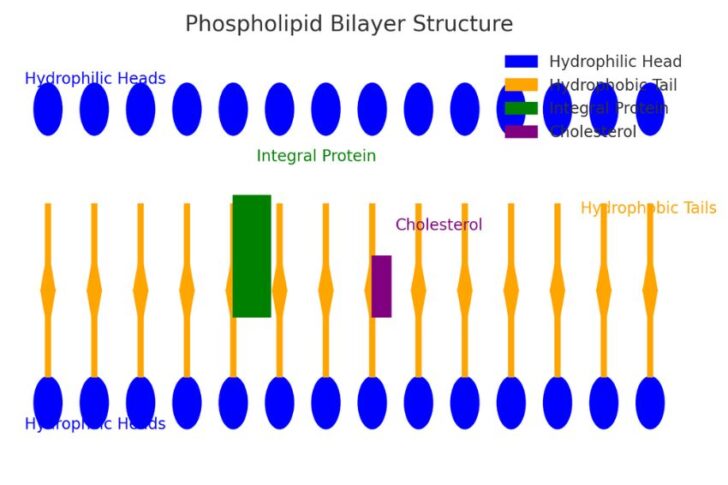
You see these principles in action all around you. The ability of our digestive system to absorb nutrients relies on protein transporters embedded in cell membranes. The way our nerves transmit signals involves ion channels made of proteins within neuronal membranes. Even the effectiveness of many medications is based on their ability to interact with specific protein receptors in our cells!
While you can't directly "experience" the phospholipid bilayer, appreciating its function can enhance your understanding of health and biology. When you learn about how certain diseases disrupt membrane protein function, or how drugs target these proteins, you gain a deeper insight into your own body. Think of it as gaining a secret superpower: the power of cellular understanding! So next time you marvel at a biological process, remember the humble phospholipid bilayer and its incredible ability to support the diverse world of proteins, making life as we know it possible.
