The First-row Transition Metal With The Most Unpaired Electrons

Hey there, eco-conscious trendsetters and science curious souls! Ever find yourself staring at a rainbow of pigments in your favorite makeup or wondering what makes that sleek metal appliance so darn strong? Well, let's dive into a little corner of the universe that's quietly powering a lot of the cool stuff around us. We're talking about the unsung heroes of the periodic table, specifically, the dazzling first-row transition metals. And today, we're on a mission to find the one that’s got the most oomph, the most spark, the most… well, unpaired electrons. Think of them as tiny little rebels, each one ready to form a bond and create something amazing.
Now, before your eyes glaze over with visions of textbooks and complicated formulas, let's keep this light and breezy. We're not aiming for a Nobel Prize lecture here; we're aiming for a vibe. A vibe that’s as cool and laid-back as a slow Sunday morning with a perfectly brewed coffee. So, grab your favorite mug, settle in, and let's unravel this electrifying mystery.
The Building Blocks of Awesome
You’ve heard of metals, right? They’re the backbone of our modern world. From the bridges we cross to the gadgets we can't live without, metals are everywhere. But the transition metals? They’re the special sauce. They sit in the middle of the periodic table, looking all sophisticated and slightly mysterious. What makes them special is their electron configuration, particularly the way their d-orbitals fill up. Think of it like a collection of little energetic dance floors, and electrons are the partygoers. When these dance floors aren't completely full, some electrons are left to their own devices, waiting for a partner. These are our unpaired electrons.
Why do we care about these lone rangers? Because they're the secret behind so many properties we take for granted. They’re responsible for metals having multiple oxidation states (meaning they can act in different ways in chemical reactions, like a chameleon of chemistry!), forming colorful compounds (hello, vibrant art supplies and stunning gemstones!), and catalyzing reactions (making things happen faster and more efficiently, like a tiny chemical accelerator).
The Contenders: A Sparkling Lineup
The first-row transition metals are a tight-knit crew, starting with Scandium (Sc) and ending with Zinc (Zn). They're like the original boy band of the periodic table, each with their own unique charm and capabilities. We’ve got Titanium (Ti), Vanadium (V), Chromium (Cr), Manganese (Mn), Iron (Fe), Cobalt (Co), Nickel (Ni), and Copper (Cu), all vying for the title of "Most Unpaired Electrons."
Let’s do a quick peek at their electron vibes. Scandium is pretty chill, with only one unpaired electron. Titanium? A bit more energetic, with two. Vanadium steps it up with three. Chromium is looking pretty interesting with a whole bunch of unpaired electrons, but it’s a bit of a special case due to its particularly stable electron configuration. Iron, the stuff of our blood and skyscrapers, has four unpaired electrons. Cobalt and Nickel are also packing some serious unpaired electron power, with three and two respectively. Copper, often seen in wiring and coins, also has a slightly more stable configuration that impacts its unpaired electron count.

And The Winner Is... Manganese!
Drumroll, please! 🥁 The crown for the first-row transition metal with the most unpaired electrons goes to… Manganese (Mn)! This powerhouse element boasts a whopping five unpaired electrons. Imagine five little electrons doing their own thing, ready to jump into action at a moment's notice. That's a whole lot of potential energy, a whole lot of bonding power!
Manganese is like the quiet achiever of the group. It might not always be in the spotlight like Iron, but its electron configuration makes it incredibly versatile and important. Think of it as the supportive friend who’s always there, ready to lend an electron (or five!).
Why Manganese is So Electrifyingly Unpaired
So, what's the secret sauce behind Manganese's electron abundance? It all comes down to its electron shell configuration. The d-orbitals, those quirky little energy levels, have space for ten electrons. Manganese, with its atomic number 25, has electrons filling these d-orbitals in a way that leaves five of them unpaired. It’s like having five empty seats at a party, and each seat is waiting for a dance partner. This abundance of unpaired electrons makes Manganese a star player in a variety of chemical reactions, especially as a catalyst.
This high number of unpaired electrons also contributes to Manganese's magnetic properties. Ever played with magnets? Well, Manganese compounds can be quite magnetic themselves, thanks to these little electron rebels. It’s a subtle, but powerful, force at play!
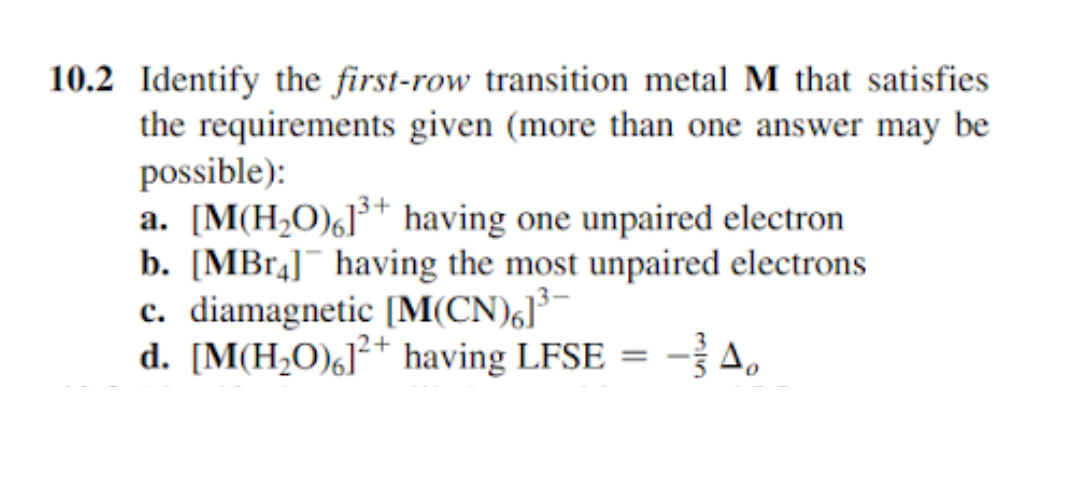
Manganese in Our Everyday Lives (You Might Be Surprised!)
You might be thinking, "Okay, cool science fact, but how does this 'Manganese' thing relate to my avocado toast and streaming binges?" Well, buckle up, because Manganese is more present in your life than you might realize!
Batteries: The Silent Powerhouses
One of Manganese's most significant roles is in the batteries that power your devices. From your smartphone to your electric car, Manganese compounds are often key components. They help facilitate the flow of electrons, which is basically what a battery does – storing and releasing electrical energy. So, next time you’re scrolling through your feed or listening to your favorite podcast, give a little nod to Manganese for keeping the juice flowing!
Steel and Alloys: The Unsung Heroes of Strength
While Iron gets all the glory for being the main ingredient in steel, Manganese is the crucial supporting actor. Adding Manganese to Iron creates steel alloys that are significantly stronger, more durable, and resistant to wear and tear. Think of the structural beams in skyscrapers, the chassis of your car, or even the cutlery you use for dinner. Manganese is often there, making them tougher and more reliable. It’s like the secret ingredient that makes good things great.
Glass and Ceramics: Adding a Splash of Color (and Clarity!)
Did you know that Manganese can be used to decolorize glass? Sometimes, impurities in glass can give it a greenish tint. Manganese compounds can counteract this, giving you that crystal-clear glass you love for your water bottles or decorative vases. But it can also be used to impart beautiful colors! Depending on how it's used, Manganese can create shades of purple, violet, and even brown in glass and ceramics. Think of those stunning stained-glass windows in ancient cathedrals or the unique glazes on artisanal pottery. That's Manganese at work!

Agriculture: Nourishing Our Food
Manganese is also an essential micronutrient for plants, playing a vital role in photosynthesis (the process plants use to make their own food) and enzyme activation. So, the fruits and vegetables you enjoy are often thanks to the presence of Manganese in the soil. It's a subtle but indispensable part of the food chain. Pretty neat, right?
Fun Fact Alert! 🤯
Did you know that Manganese is named after the Latin word magnes, meaning "magnet"? This is a nod to its magnetic properties and its association with other magnetic minerals like Magnetite (iron oxide).
The Electron Dance: A Metaphor for Connection
Looking at these unpaired electrons, it’s easy to see them as individual entities. But in reality, they’re all about connection. They’re the bits of an atom that are most eager to interact, to form bonds, and to create something bigger and more complex than themselves. It’s a constant dance of attraction and reaction.
Think about it in terms of our own lives. We all have those moments, those unique skills, those passions that make us feel a little bit… unpaired. We have our own individual spark. But it's when we connect with others, when we share our talents and energy, that we create truly amazing things. Whether it's a collaborative project at work, a shared hobby with friends, or simply offering a helping hand, those connections are what build our communities and enrich our lives.

Chromium vs. Manganese: A Friendly Rivalry
Now, you might be wondering about Chromium (Cr). It's often cited as having a lot of unpaired electrons too, and indeed it does, often appearing with six. However, Manganese holds the record for the most, with its five unpaired electrons being particularly stable in certain configurations. It's like a friendly race where Manganese just edges out the competition for this specific title!
Chromium is also a rockstar, responsible for the shiny chrome plating on cars and bikes, and a key component in stainless steel. It’s a testament to how different electron arrangements lead to different, but equally important, properties.
Embracing the Unpaired in Our Own Lives
So, what’s the takeaway from this deep dive into the world of unpaired electrons and the mighty Manganese? It’s a reminder that even in the seemingly rigid structure of science, there’s a dynamic, energetic quality. And perhaps, more importantly, it’s a metaphor for us. We all have our unique strengths, our individual quirks, those parts of us that are ready to engage and create. And just like Manganese, the more we're open to these connections, the more we can contribute to the vibrant tapestry of the world around us.
The next time you see a vibrant color, use a strong piece of metal, or charge your phone, take a moment to appreciate the unseen forces at play. The world is full of fascinating elements, each with their own story and their own way of contributing to the grand design. And sometimes, the most powerful things are born from those who are a little bit unpaired, ready to create something extraordinary together.
