The Body's Electrochemical Communication Circuitry Is Known As The
Hey there! Grab your mug, settle in, we’re about to spill the tea on something seriously cool happening inside you right now. Like, constantly. Ever stop to think how your brain actually tells your hand to, you know, pick up that coffee? It's not magic, though sometimes it feels like it, right? It’s this incredible, intricate little party happening 24/7. And guess what? We're going to chat about the star of the show, the absolute MVP of your insides.
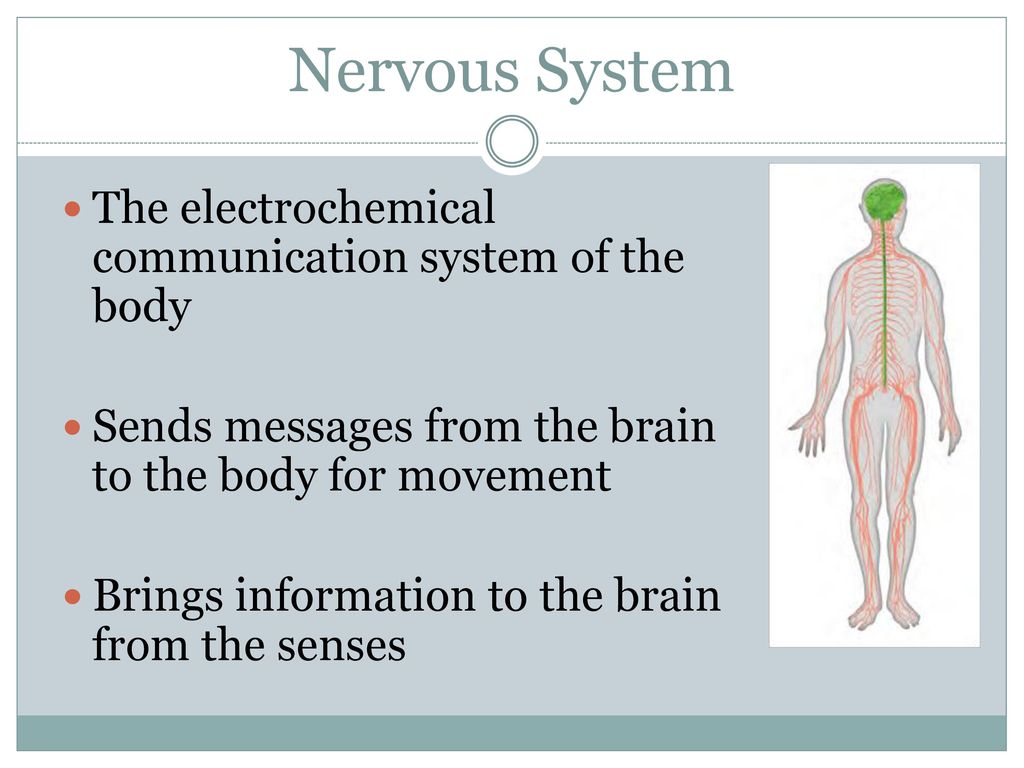
So, what is this amazing system that’s making all your bodily actions, thoughts, and even those random itches happen? Drumroll, please! It’s known as the body's electrochemical communication circuitry. Fancy, huh? But don't let the big words scare you. Think of it like the ultimate, super-fast, organic Wi-Fi network. Your body’s own built-in internet, but way more important than cat videos, believe it or not.
Seriously, imagine a world without it. No wiggling your toes? No tasting that delicious cookie? No feeling that surge of joy when your favorite song comes on? Shudder. We’d be like… very still, very quiet statues. And nobody wants that, right? So, this whole electrochemical thing? It’s pretty crucial.
What exactly is electrochemical, though? Let's break it down, because it's actually kind of brilliant. You've got your electrical side, which is all about tiny impulses zipping around. Think of it like little sparks. And then you’ve got your chemical side, which involves special molecules, little messengers carrying signals. It's this dynamic duo, this constant back-and-forth, that keeps everything running smoothly.
At the heart of this whole operation are these amazing little guys called neurons. Ever heard of them? They’re like the wires in your electrical circuit, but way more sophisticated. They're the fundamental building blocks of your nervous system. And guess what? You have billions of them! BILLIONS. That’s a lot of tiny messengers, wouldn't you say?
These neurons are like super-specialized telephone operators, but instead of taking your order for pizza, they're relaying vital information. From the tip of your toe all the way to the deepest parts of your brain. It's a seriously impressive network, if you ask me.
So, how does this electrical magic happen? Well, neurons have these special properties. They can generate and conduct electrical impulses. We’re talking about tiny electrical charges that travel down the length of the neuron. It's like a tiny lightning bolt, but much, much smaller and safer, thankfully. Otherwise, we'd all be sparking like disco balls!

These electrical signals are called action potentials. Catchy name, right? And they are the rapid, short-lived changes in the electrical potential across the membrane of a neuron. Basically, it’s the neuron saying, "Hey! I have something important to tell you!"
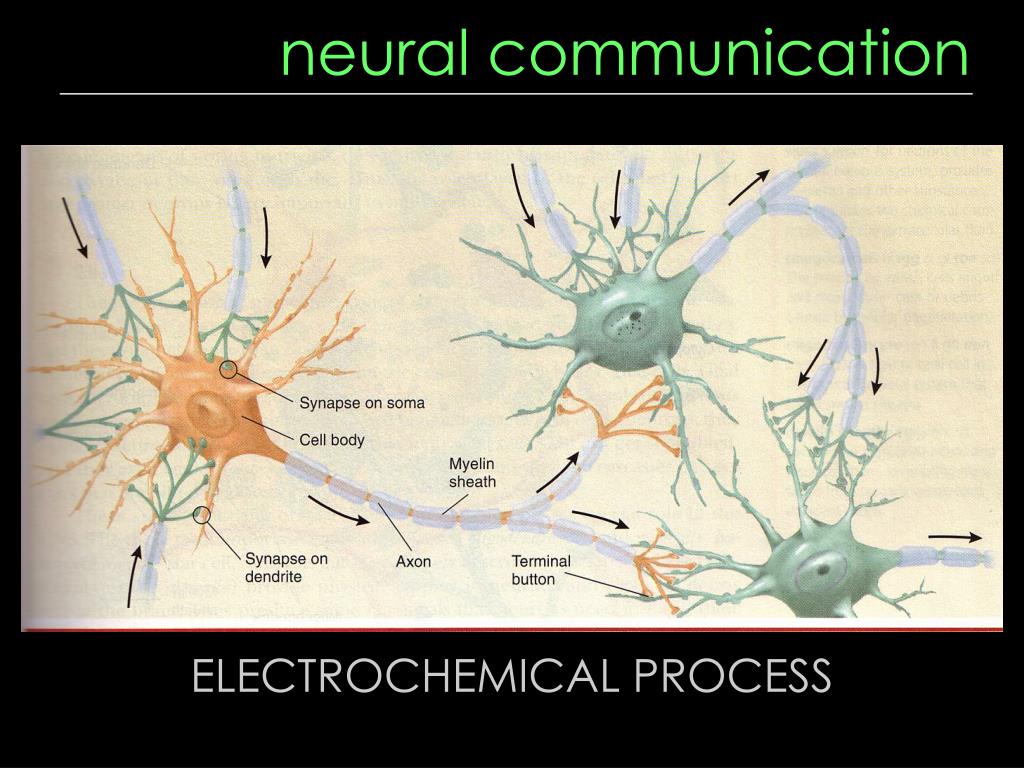
But here's where the chemical part really kicks in, and it's honestly mind-blowing. Neurons don't directly touch each other. Nope. There's a tiny gap between them called a synapse. It's like a little bridge that needs a special delivery service to get the message across.
When that electrical impulse reaches the end of one neuron, it triggers the release of these chemical messengers. These are called neurotransmitters. Think of them as little chemical couriers, sailing across that synaptic gap. Super important job, wouldn't you agree? They’re the unsung heroes of your brain, carrying out all the important conversations.
These neurotransmitters then bind to receptors on the next neuron. It’s like a lock and key situation. The neurotransmitter is the key, and the receptor is the lock. When the right key fits the right lock, it causes a change in the receiving neuron. This can either excite it, making it more likely to fire its own electrical signal, or inhibit it, making it less likely.
It's this constant dance of electrical impulses and chemical signals that allows for the incredible complexity of your thoughts, feelings, and actions. You think about picking up that cookie, and BAM! A cascade of electrochemical signals is already underway, telling your muscles to move. It’s faster than you can say "chocolate chip."
Let's talk about some of these neurotransmitters, because they’re fascinating characters. You’ve got dopamine, which is often associated with pleasure and reward. Ever feel that rush of satisfaction after accomplishing something? That's dopamine at play, cheering you on! It’s like your brain’s personal cheerleader.
Then there's serotonin, which plays a big role in mood regulation, sleep, and appetite. Ever feel a bit down or a bit too hungry? Serotonin might be having a little moment. It’s like the calm, steady presence in the room.
And we can’t forget acetylcholine! This one is crucial for muscle contraction. So, every time you twitch, blink, or do that fancy coffee-stirring move, acetylcholine is on the job. It’s the conductor of your muscle orchestra.
These are just a few examples, of course. There are dozens of different neurotransmitters, each with its own unique function and effect. It’s like a whole chemical symphony playing out in your head, all the time. And the conductors are these amazing neurons, working tirelessly.
The amazing thing is, this isn't just happening in your brain. This electrochemical communication circuitry extends throughout your entire body. Your peripheral nervous system, which is everything outside your brain and spinal cord, is all about these signals. Your nerves are essentially bundles of neurons carrying messages to and from your brain.

So, when you touch something hot, that’s a quick electrochemical signal shooting from your fingertips all the way up your arm, to your spinal cord, and then to your brain, yelling "YOWZA! HOT!" And just as quickly, another signal races back telling your hand to get away from there, you silly goose! It’s instinct, but it’s all powered by this electrochemical magic.
Think about your heart beating. It doesn’t just decide to go "thump-thump" randomly. There's a precise electrical system within your heart that controls the rhythm. And neurotransmitters are involved in speeding it up or slowing it down, depending on what you're doing. So, if you're running for the bus, your heart gets a little electrochemical nudge to pick up the pace. If you're napping, it’s told to take it easy.
Even your digestive system, that often-underappreciated part of your body, relies heavily on electrochemical communication. The signals help move food along, release digestive juices, and tell you when you’re full. It’s a whole complex system that we rarely think about, but it's humming with electrochemical activity.
What’s truly mind-boggling is the speed of all this. These electrical impulses can travel at speeds of up to 268 miles per hour! That's faster than a Formula 1 car. Imagine trying to send a text message that fast. You'd be finished before you even finished typing. It's a testament to the efficiency of this biological system.
And it's all so elegantly designed. The structure of a neuron, with its long axon and branching dendrites, is perfectly suited for transmitting and receiving these signals. The tiny synaptic cleft ensures that the chemical signals are delivered efficiently, without too much diffusion. It's nature's engineering at its finest, wouldn't you say?

This electrochemical circuitry is also incredibly adaptable. It can change and adapt based on your experiences. This is the basis of learning and memory. When you learn something new, you're actually changing the connections between your neurons, or strengthening existing ones. It’s like rewiring your brain, but in a good way!
Think about learning to ride a bike. At first, it’s clumsy and wobbly. But with practice, those electrochemical pathways become more efficient. Your brain gets better at coordinating the signals needed for balance and pedaling. You’re literally building a better communication circuit through practice. Pretty neat, huh?
Even something as simple as your senses are all about this communication. Light hitting your eyes? Electrochemical signals are sent to your brain, and voilà! You see. Sound waves hitting your ears? Yep, you guessed it – electrochemical signals painting a picture of the world around you. It’s a constant stream of information, interpreted and processed by this incredible system.
The complexity of this electrochemical communication circuitry is what makes us, well, us. It’s what allows for consciousness, emotions, creativity, and all the unique qualities that make each of us an individual. It’s not just about sending signals; it's about the intricate patterns and the way these signals interact.
So, next time you take a sip of your coffee, or laugh at a joke, or even just feel a gentle breeze on your skin, take a moment to appreciate the incredible electrochemical communication happening within you. It's a constant, silent, and utterly vital dance that keeps you alive and experiencing the world. It’s your body’s own private, super-speed, biological internet. And you’re the only one who has it. Pretty amazing, right? Keep those signals flowing, folks!
