Student Exploration Distance Time And Velocity Time Graphs
Ever found yourself wondering how fast that bus is really going, or how long it will take to get to your destination without actually watching the clock tick by? Or maybe you're the kind of person who loves puzzles and figuring out how things work? Well, then you're in luck, because we're about to dive into the wonderfully insightful world of distance-time and velocity-time graphs. These aren't just dry diagrams for science class; they're actually incredibly useful tools that help us understand and predict movement all around us, making everyday life a little bit clearer and a lot more interesting.
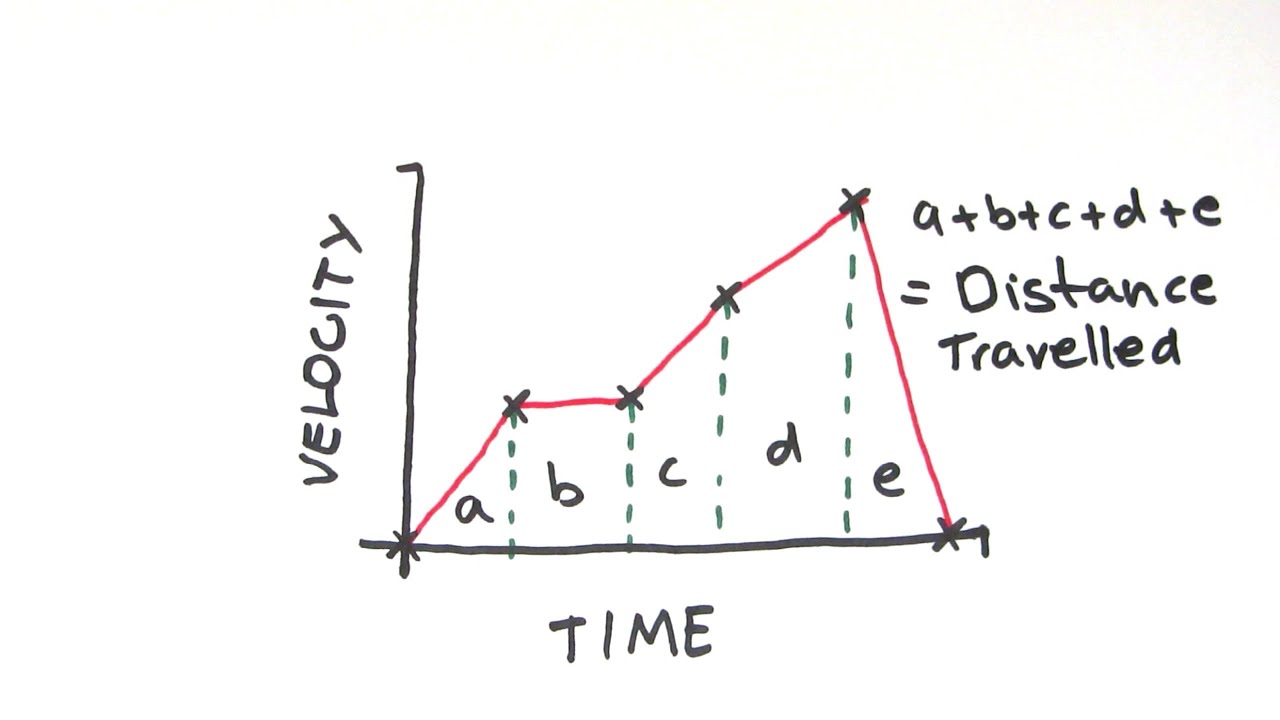
Think about it. From planning your commute to estimating how long your pizza delivery will take, understanding how distance, time, and velocity relate is fundamental. These graphs are essentially visual stories of motion. A distance-time graph tells you where something is at any given moment. Is it moving? Standing still? How fast is it covering ground? Conversely, a velocity-time graph focuses on the speed and direction of an object. Is it accelerating? Decelerating? Maintaining a constant speed? This knowledge is invaluable!
You're using these principles every day, even if you don't realize it. When you check your GPS app, it's calculating your distance to your destination and estimating the time of arrival based on your current velocity (and traffic, of course!). Sports fans use these concepts implicitly to gauge player speed and track race progress. Even something as simple as packing for a trip involves estimating the time it will take to get somewhere, which is directly related to your intended travel velocity.
So, how can you get more out of these fantastic graphing tools? First off, don't be intimidated. Start with simple examples. Imagine a toy car rolling across a table. You can easily track its distance over specific time intervals and then plot it. Look for patterns. A straight line on a distance-time graph means constant velocity. A curved line? That means the speed is changing – acceleration or deceleration! For velocity-time graphs, a flat line indicates constant speed, while a sloped line shows acceleration.
Try to apply it to your own experiences. Next time you're walking, jogging, or cycling, try to mentally sketch out what your distance-time or velocity-time graph might look like. Where are the steep slopes? Where are the flat parts? What does that tell you about your effort and speed? Visualize the motion as you look at the graph. This active engagement will make the concepts stick much better. Most importantly, have fun with it! These graphs are like decoding the secret language of movement. The more you practice, the more you'll see the world around you in a new, dynamic way. It’s a bit like becoming a motion detective!
