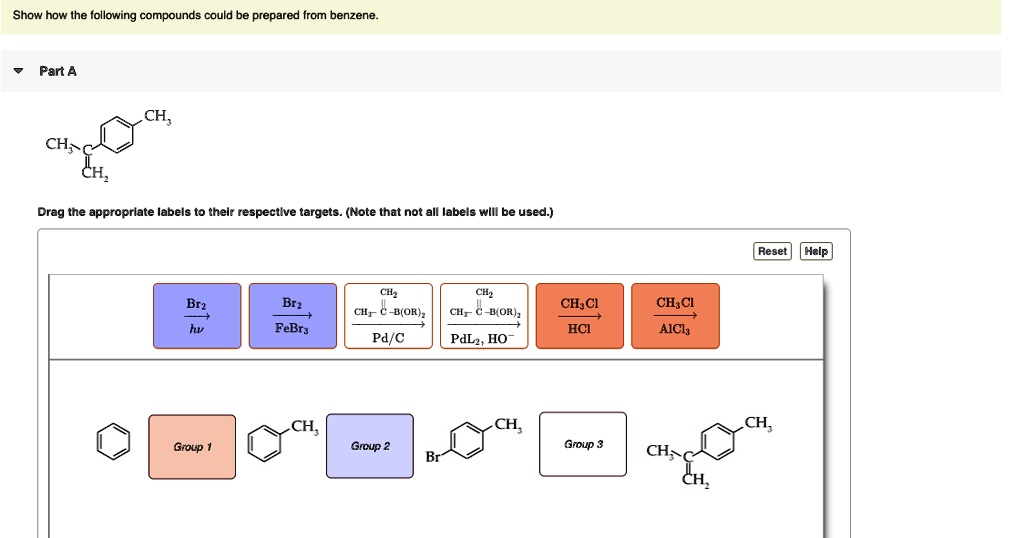
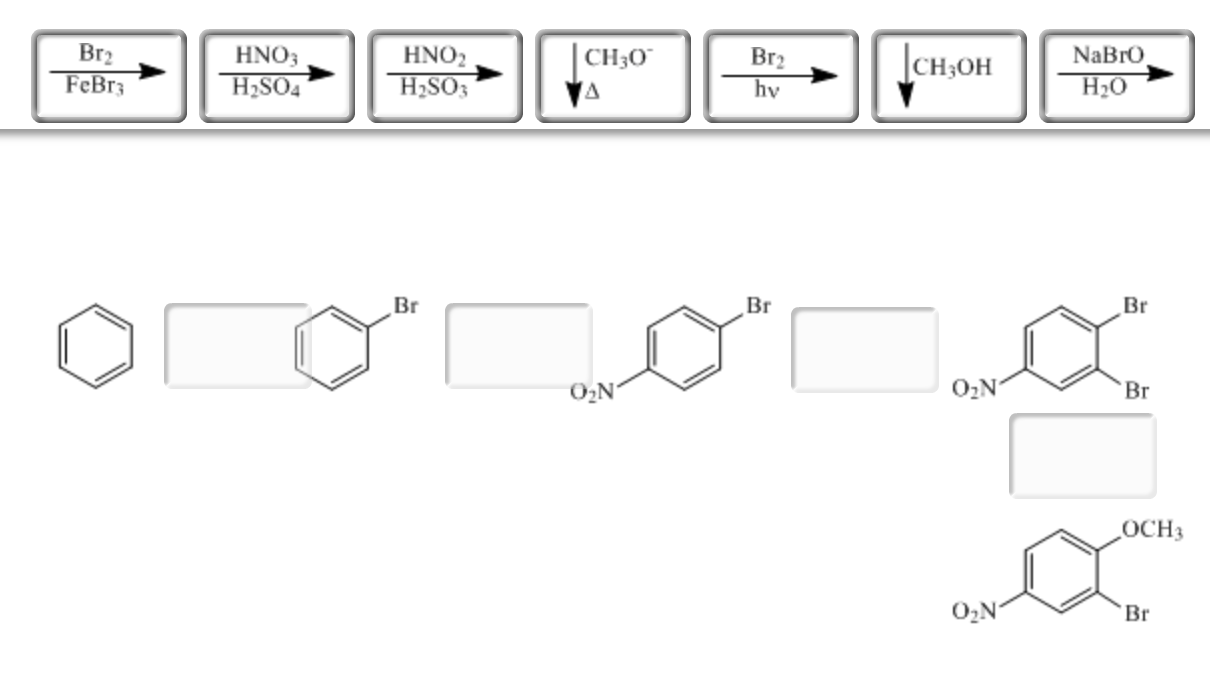
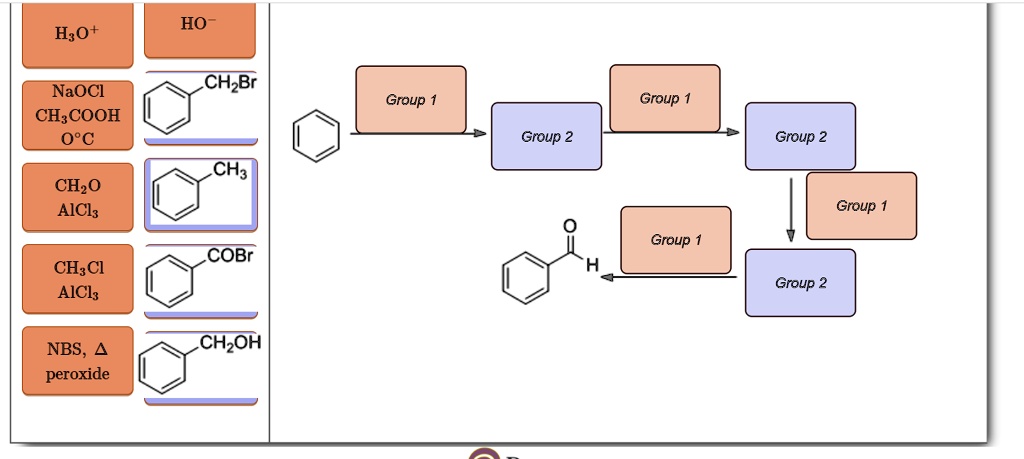
Show How The Following Compounds Could Be Prepared From Benzene
Ever looked at a simple ring of six carbon atoms and wondered what amazing things it could become? That’s the magic of benzene, folks! It’s like the ultimate starting point in chemistry, a humble little molecule that can transform into a dazzling array of useful and interesting compounds. Think of it as a blank canvas, ready to be painted with all sorts of functional groups, leading to incredible discoveries and everyday products. It’s truly a chemistry superhero, quietly enabling so much of what we use and know.
Let's dive into how this plain-looking ring can morph into some truly special molecules. It’s not some complicated, intimidating process. Think of it more like a fun recipe, where we add a few key ingredients and follow some straightforward steps. The results, however, are anything but ordinary. We're talking about transforming a basic building block into things that can make our lives easier, healthier, and even a little more colorful!
One of the easiest and most common transformations for benzene is making something called nitrobenzene. Imagine taking our benzene ring and giving it a little "nitro" boost. This is usually done with a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid. It’s a bit like a chemical handshake, where the nitric acid attaches itself to the benzene ring. The sulfuric acid is like the helpful friend that makes the whole process run smoothly. Nitrobenzene itself is a pretty important intermediate, meaning it's a stepping stone to even more exciting things. It has a slightly sweet smell, which is a fun little characteristic, but don't be fooled – it's a chemical that needs to be handled with care!
Now, what can we do with this nitrobenzene? Well, here’s where the real fun begins! We can take that "nitro" group and change it into an "amino" group. This process, called reduction, is like giving the molecule a makeover. We can achieve this by reacting nitrobenzene with something like hydrogen gas in the presence of a metal catalyst, or even by using iron and acid. The result? Aniline! This is where things get really interesting. Aniline is a fundamental building block for so many things we encounter daily. Think about the vibrant colors in your clothes or the dyes used in inks. Yep, aniline is often the starting point for those!
Let's talk about those colors for a moment. The ability to create vibrant and lasting colors is one of the most captivating aspects of organic chemistry, and aniline plays a starring role. Imagine going from a plain white shirt to one in a stunning shade of blue or red. That transformation often starts with the humble benzene ring, which is then transformed into aniline. From there, a whole world of colorful compounds opens up. It’s like aniline has a secret ingredient that lets it team up with other molecules to create hues that delight our eyes. It’s a beautiful example of how a simple chemical can lead to such visible and joyful results.
But the story doesn’t stop at dyes. Aniline is also crucial for making pharmaceuticals. Many medicines that help us feel better and live longer have a backbone that originated from aniline. It's a testament to the versatility of this benzene derivative. It's pretty amazing to think that a molecule that started as a simple ring can contribute to something as vital as human health.
Another interesting path from benzene involves adding a halogen, like chlorine or bromine. This is typically done using a Lewis acid catalyst, such as iron(III) chloride or aluminum chloride. It’s like attaching a little handle to our benzene ring. For example, reacting benzene with chlorine gas in the presence of iron(III) chloride gives us chlorobenzene. This might sound a bit technical, but think of chlorobenzene as another versatile intermediate. It’s a bit like a jack-of-all-trades, ready to be modified further.
It's fascinating how a few simple reactions can unlock so much potential from a single molecule!
What can we do with chlorobenzene? Lots of things! It can be used to make other interesting compounds, like phenols. Phenols are important in disinfectants and also in the production of plastics. So, that simple addition of chlorine can lead to materials that keep our environments clean and help build the world around us. It’s a clever way to add functionality and open up new possibilities.

Then there's the world of alkylbenzenes. Imagine sticking a chain of carbon atoms onto our benzene ring. This is often done through a process called Friedel-Crafts alkylation. You take benzene and react it with an alkyl halide (like ethyl chloride) in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst. Voila! You get an alkylbenzene, like ethylbenzene. This might sound like just adding a bit of length, but it dramatically changes the properties of the molecule. Ethylbenzene, for instance, is a precursor to styrene, which is the monomer used to make polystyrene. Yes, that ubiquitous plastic used in packaging, insulation, and so much more!
It’s quite remarkable how a single starting molecule, benzene, can branch out into so many different directions. It’s like a tree with numerous branches, each leading to a unique and valuable destination. The beauty lies in the elegant simplicity of the reactions and the profound impact of the resulting compounds. From the vibrant colors that brighten our world to the materials that shape our daily lives and the medicines that improve our health, the journey from benzene is a truly captivating adventure in chemistry. It's a constant reminder of the incredible power and creativity inherent in the molecular world, just waiting to be explored!
