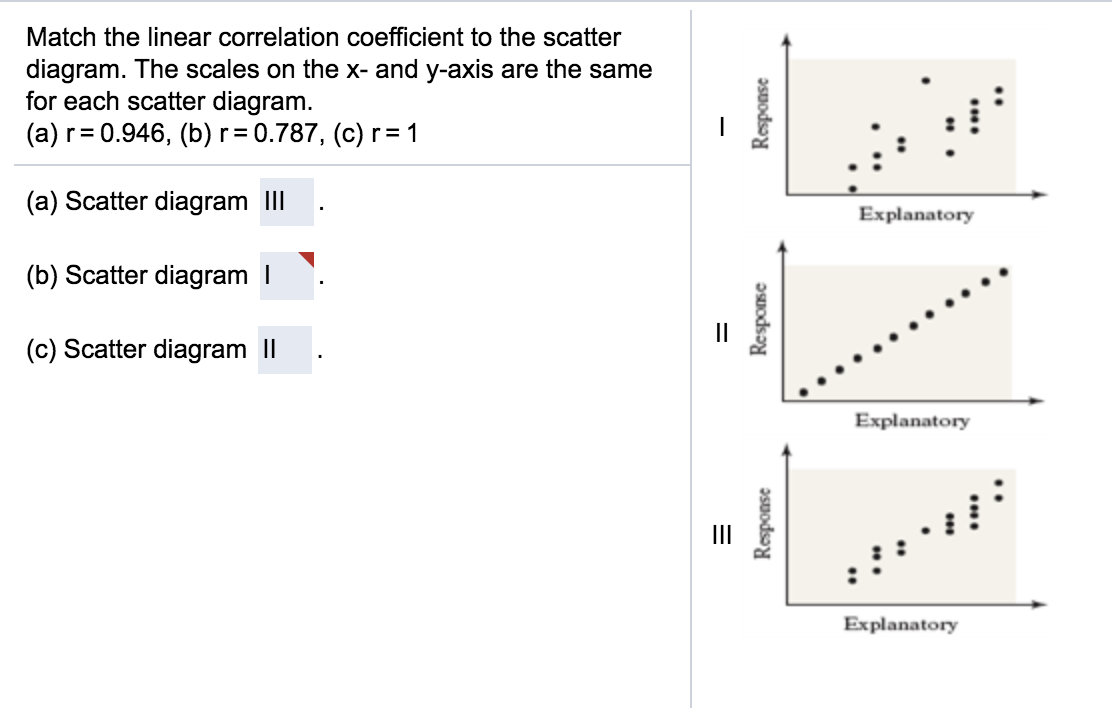
Match The Linear Correlation Coefficient To The Scatter Diagram. R
Ever find yourself staring at a bunch of dots on a graph and thinking, "What's the story here?" You're not alone! Many of us are drawn to the visual appeal of scatter diagrams, and there's a fun, intuitive way to connect them with their underlying mathematical narrative: matching them to their linear correlation coefficients. It's like a puzzle, but with a purpose that can actually make your everyday life a little clearer and a lot more interesting. People enjoy this activity because it taps into our innate desire to find patterns and understand relationships, all without requiring a Ph.D. in statistics.
So, what's the big deal about this "R"? The linear correlation coefficient, often represented by the letter R, is a number that tells us the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two sets of data. Think of it as a score. An R value of +1 means a perfect positive linear relationship – as one thing goes up, the other goes up perfectly in step. An R of -1 signifies a perfect negative linear relationship – as one goes up, the other goes down perfectly. Values closer to 0 suggest a weak or no linear relationship. This simple number unlocks a treasure trove of understanding.
Why should you care about matching scatter diagrams to their R values? Because understanding correlations helps us make better decisions in countless aspects of life. Imagine you're trying to figure out if studying more leads to better grades. A scatter plot of hours studied versus test scores, paired with its R value, could tell you! If R is close to +1, it's a strong indicator. This principle applies everywhere: Is there a correlation between the amount of exercise and weight loss? Does advertising spending correlate with sales increases? Even simple things, like seeing if more time spent on social media correlates with less sleep, can be illuminated.
The beauty of matching scatter diagrams and R values is that it's incredibly visual and accessible. You don't need complex formulas to start grasping the concept. Look at the general trend of the dots. Are they sloping upwards from left to right? That's a positive correlation. Sloping downwards? That's negative. Are they tightly clustered around an imaginary line? That indicates a strong correlation. Are they scattered randomly like confetti? That suggests a weak or non-existent linear relationship. The closer the dots hug that imaginary line, the higher the absolute value of R will be (closer to 1 or -1). The more spread out they are, the closer R will be to 0.
To make your experience more enjoyable and effective, try thinking of it as a game. Start with simple examples you can easily visualize. For instance, try matching scatter plots of things like: the height of a person and their shoe size (likely a positive correlation), the speed of a car and the time it takes to travel a set distance (a negative correlation), or the number of rainy days and the number of beach trips (likely a weak or negative correlation). Don't be afraid to guess! The more you practice, the more intuitive it becomes. You'll start spotting patterns and understanding the stories hidden within the data, making this seemingly abstract concept a genuinely useful tool for navigating our data-rich world.
