Match Each Function With The Correct Cytoskeletal Structure
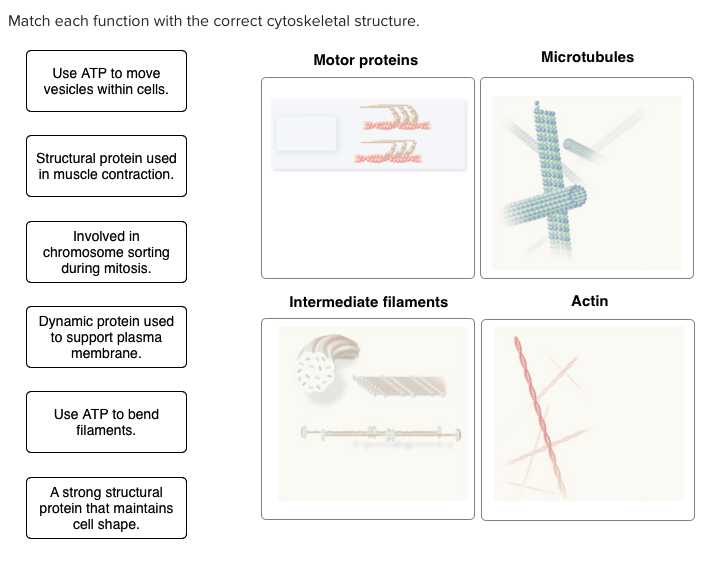
Alright, so imagine your cells are tiny little cities. And just like any bustling metropolis, they've got their infrastructure. We’re not talking about potholes and dodgy public transport here, oh no. We’re talking about the microscopic marvels that keep everything zipping along: the cytoskeleton! It’s the cellular equivalent of a construction crew, a personal trainer, and a moving company all rolled into one. And it's not just one boring old dude doing all the work; it's a team of specialists, each with their own unique gig.
Let’s dive into the wonderful world of these cellular superstars. Forget building blueprints for a sec, and think more along the lines of… well, what makes a cell tick? It’s these protein fibers, and trust me, they’re more exciting than they sound. Think of them as the unsung heroes of your insides, holding it all together, letting you, you know, exist.
The Cytoskeleton: Your Cell's Personal Support System
So, what exactly is this cytoskeleton? It’s a dynamic network of protein filaments and tubules in the cytoplasm of many living cells, giving them shape and coherence. It's literally what stops your cells from collapsing into a sad, amorphous blob. Imagine trying to build a house out of jelly. Not ideal, right? Well, the cytoskeleton is the sturdy scaffolding that prevents cellular jelly-ness.
Now, the real fun begins when we start talking about the different types of these protein structures. It’s like a superhero team, each with their own power set. We’ve got the big, burly ones, the fast and agile ones, and the ones that are just… everywhere. And if you get them mixed up, well, let’s just say your cell might have a slight identity crisis. So, let’s play a little matching game, shall we? Think of it as speed dating for cellular components.
Microfilaments: The Speedy Movers and Shakers
First up, we have the microfilaments. These guys are the smallest of the bunch, about 7 nanometers in diameter. Don’t let their size fool you, though! They’re like the tiny, hyperactive squirrels of the cell. Made primarily of a protein called actin, they’re all about movement and shape changes. Think of them as the cellular equivalent of those little motorized scooters you see whizzing around cities.
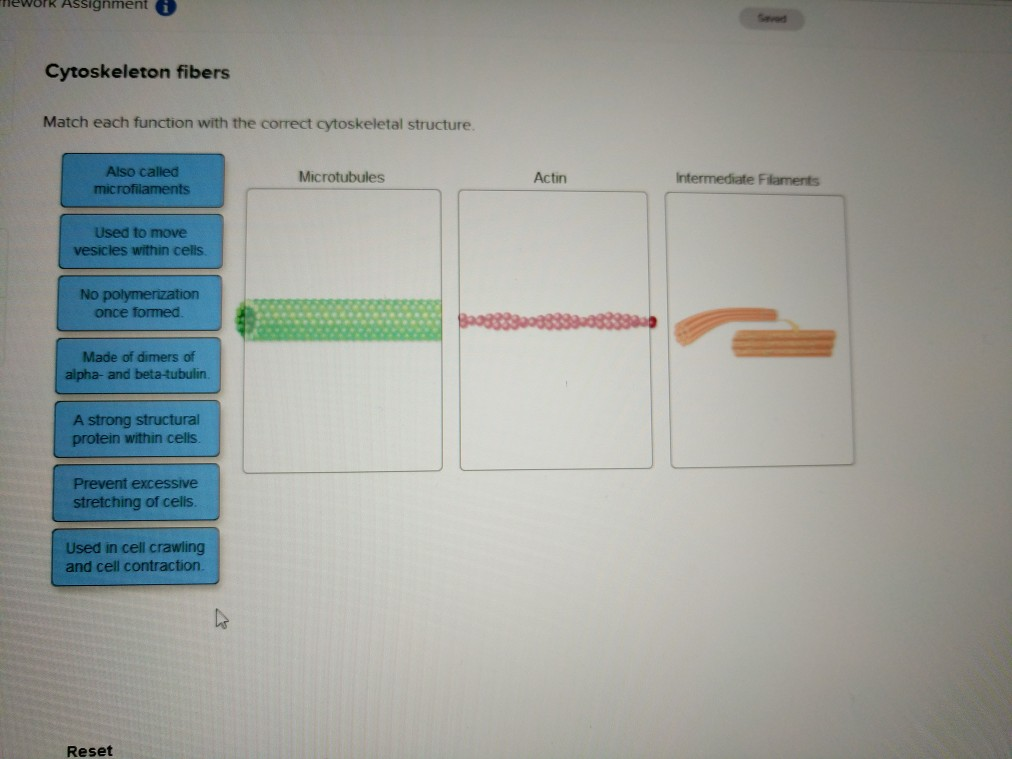
What do they do? Oh, just a few crucial things. They’re involved in cell crawling – you know, when a cell needs to ooze its way from point A to point B. Imagine a single-celled organism doing the limbo. That’s microfilaments at work! They also help form those little finger-like projections called microvilli, which you find in places like your intestines, soaking up all those delicious nutrients. So, next time you’re enjoying a tasty meal, give a little nod to your actin filaments for their hard work.
And get this, they’re also the ones responsible for muscle contraction. Yep, those powerful muscles that let you lift your coffee cup (or, you know, run a marathon) rely heavily on the interplay of actin and another protein called myosin, which works like tiny molecular engines attached to the microfilaments. It's a real tug-of-war, but a very organized one!
Intermediate Filaments: The Tough Guys of the Neighborhood
Next on our cellular roster are the intermediate filaments. As their name suggests, they’re somewhere in the middle in terms of size, ranging from 8 to 12 nanometers. These guys are the stoic, reliable backbone of the cell. They’re not as flashy as the microfilaments, and they’re not as big as the next guys, but they are incredibly tough. Think of them as the reinforced concrete of the cellular city.
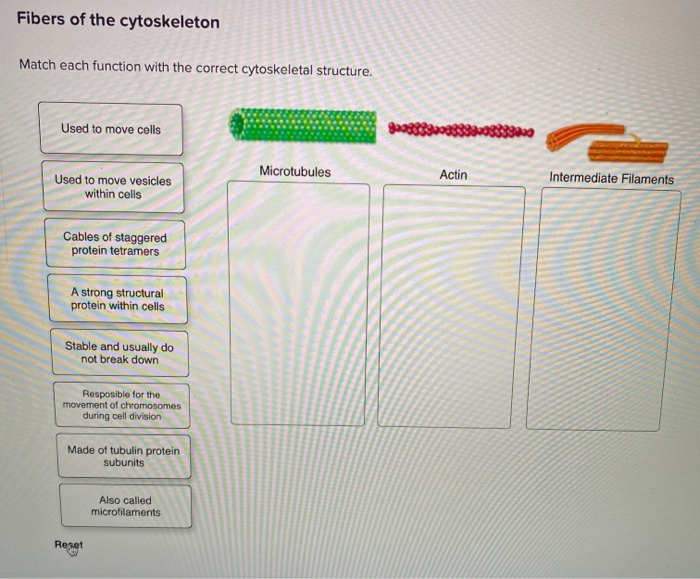
What’s their main gig? Mostly providing mechanical strength and resisting stretching. They’re like the bouncers of the cell, ensuring it doesn’t get too squished or ripped apart. They form a network throughout the cytoplasm and are particularly important in cells that are subjected to a lot of stress, like skin cells. Ever wonder why your skin is so resilient? Thank your intermediate filaments!
They are made up of a diverse group of proteins, depending on the cell type. For instance, in skin cells, you’ll find a protein called keratin – yep, the same stuff that’s in your hair and nails! It’s like your hair and nails are actually part of your cellular armor. How cool is that? These filaments help anchor organelles, the little organs within the cell, in place. They prevent things from just floating around willy-nilly. It’s a well-organized cellular workspace, people!
Microtubules: The Cellular Highways and Organizers
Finally, we have the heavy hitters: microtubules. These are the biggest of the bunch, with a diameter of about 25 nanometers. They’re like the superhighways of the cell, providing tracks for things to travel on. Made of a protein called tubulin, they’re hollow tubes that are constantly being assembled and disassembled, depending on the cell’s needs. Imagine a city with a constantly reconfiguring subway system – that’s microtubules!
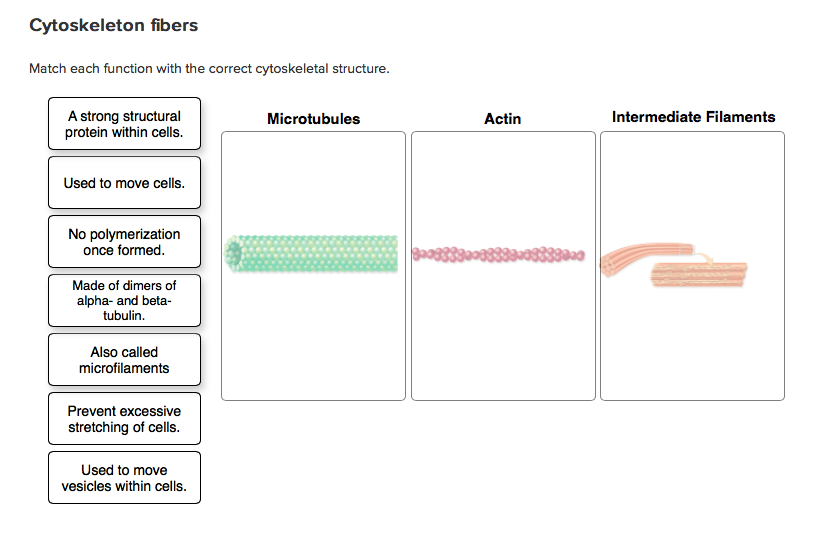
What are their major responsibilities? Well, they’re crucial for maintaining cell shape, but their starring role is in intracellular transport. They act as tracks for motor proteins, like tiny little delivery trucks, to carry vesicles and organelles to different parts of the cell. This is how your cell gets its groceries, so to speak. Without microtubules, your cellular delivery service would grind to a halt, and that’s a recipe for cellular disaster.
But wait, there’s more! Microtubules are also the architects of the mitotic spindle, the structure that segregates chromosomes during cell division. So, when your cells are busy multiplying (which, thankfully, they do!), microtubules are the unsung heroes making sure each new cell gets a complete set of genetic material. They are also the structural basis of cilia and flagella, those whip-like appendages that some cells use for locomotion. Think of paramecia doing a synchronized swimming routine; that’s microtubules powering them!
The Grand Cellular Shuffle: Matching Our Heroes
So, let’s recap and make sure we’ve got our cellular heroes assigned to their proper duties. It’s like a cosmic game of musical chairs, but with protein filaments.
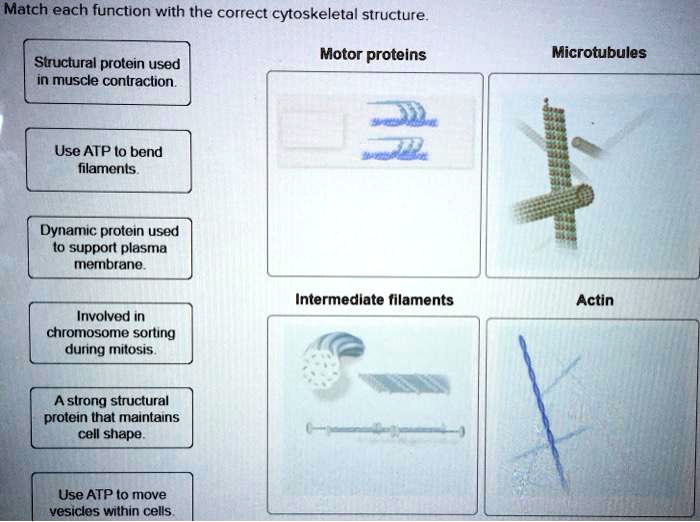
Function Spotlight: What’s Your Superpower?
Let’s see if you can match these vital cellular tasks to the right cytoskeletal element. Ready? No peeking at the answers below!
- Providing mechanical strength and resisting stretching – Think tough, think resilient.
- Intracellular transport of vesicles and organelles – Think highways, think delivery trucks.
- Cell crawling and muscle contraction – Think movement, think rapid change.
- Forming the mitotic spindle for chromosome segregation – Think cell division, think genetic distribution.
- Maintaining cell shape and anchoring organelles – Think scaffolding, think structural integrity.
Okay, time for the big reveal! Let’s see if your cellular matchmaking skills are up to par.
The Answers: Who Does What?
- Providing mechanical strength and resisting stretching – This is the domain of the intermediate filaments. They are the tough cookies, the shock absorbers of the cellular world. They’re built to last and to take a beating.
- Intracellular transport of vesicles and organelles – Our speedy delivery service, the microtubules, are on this. They provide the tracks for those motor proteins to ferry goods all over the cell. Essential for keeping the cellular economy humming!
- Cell crawling and muscle contraction – These are the movers and shakers, the microfilaments! They enable those amoeba-like oozes and the powerful contractions of your muscles. They’re all about dynamic action.
- Forming the mitotic spindle for chromosome segregation – This critical task during cell division is handled by the microtubules. They organize the chaos of cell division to ensure accuracy. Talk about a high-stakes job!
- Maintaining cell shape and anchoring organelles – While all cytoskeletal elements contribute to cell shape, the intermediate filaments are particularly key for overall structural integrity and holding things in place, acting as a stable internal framework. And let’s not forget, microtubules also play a significant role in defining cell shape. It's a team effort, but intermediate filaments are the steady anchors.
See? It’s not just a bunch of complicated science jargon. It’s a fascinatingly organized system where every protein filament has a crucial role. So, the next time you marvel at the complexity of life, give a little shout-out to your cytoskeleton. It’s working tirelessly behind the scenes, keeping you, your cells, and everything they do, in perfect working order. And that, my friends, is pretty darn awesome.
