Find The Indicated Probability Using The Standard Normal Distribution.
Hey there, coffee buddy! So, you've been wrestling with this whole "standard normal distribution" thing, huh? Don't worry, it sounds way scarier than it is. Think of it as our little secret weapon for understanding all sorts of stuff, from how tall people are to, well, a whole bunch of other random but surprisingly important things.
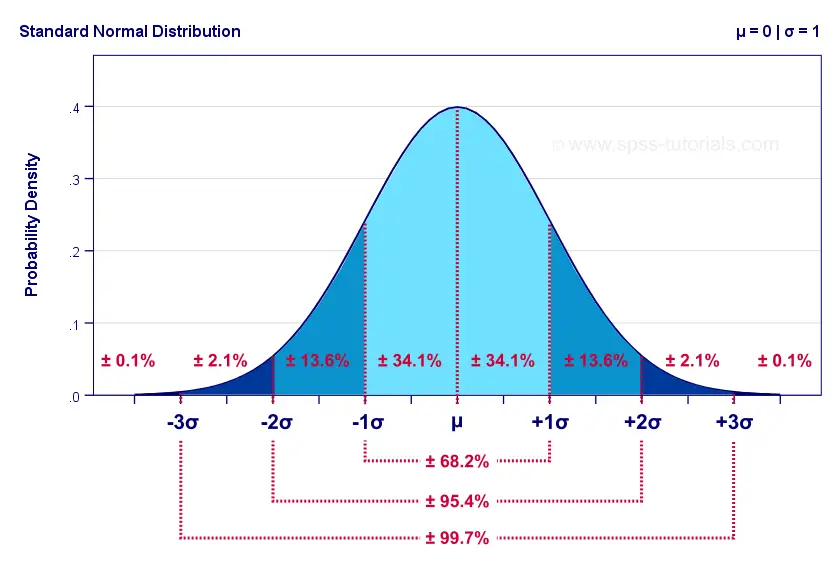
Basically, we're talking about a bell curve. Yeah, you know, that classic shape that looks like, surprise, a bell! It's symmetrical, perfectly balanced, and where most of the data hangs out in the middle. Pretty neat, right?
And the "standard" part? That just means we've done some fancy math to make things super simple. We're talking about a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one. It's like the "vanilla" flavor of normal distributions. Easy peasy.
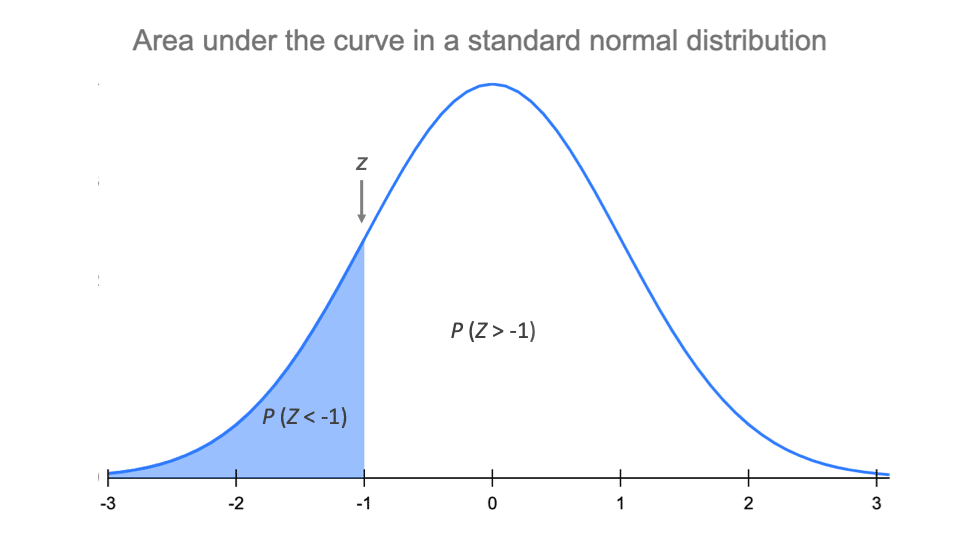
So, how do we actually find probabilities with this thing? That's where our trusty Z-score comes in. Think of the Z-score as a translator. It tells you how many standard deviations away from the mean your particular data point is. Positive Z-score? You're above average. Negative? You're a bit below. Zero? You're right smack in the middle. Goldilocks zone!
We get our Z-score by using this little formula: Z = (X - μ) / σ. Don't let the Greek letters scare you! X is just your data point, μ (that's 'mu') is the mean, and σ (that's 'sigma') is the standard deviation. See? Not so bad!
Once you've got your Z-score, the magic happens. We whip out a Z-table. This isn't some ancient scroll of forbidden knowledge, okay? It's just a handy chart that tells you the probability of getting a Z-score less than or equal to the one you calculated. It's like a cheat sheet for the bell curve!
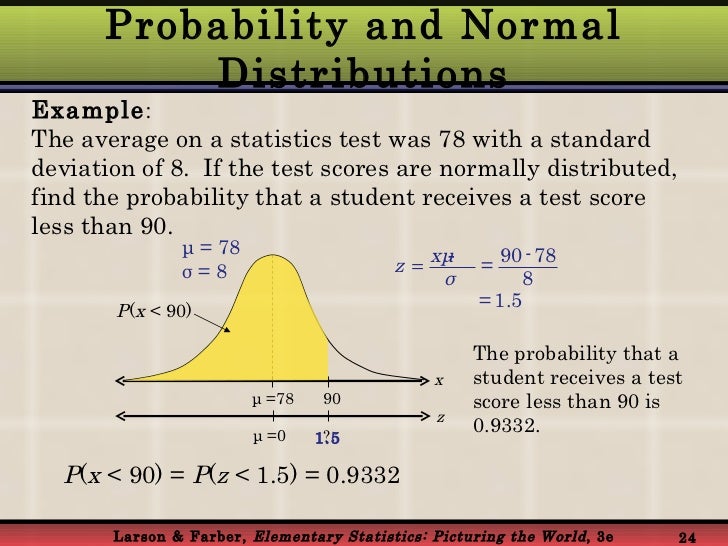
Imagine you want to know the probability of a student scoring less than 85 on a test. Let's say the average score (the mean) was 70, and the standard deviation was 10. First, you'd calculate your Z-score: Z = (85 - 70) / 10 = 1.5. Easy, right? That means 85 is 1.5 standard deviations above the average.
Now, you grab your Z-table (you can find these online everywhere, no need to hunt in dusty libraries!). You look up 1.50. Boom! The table will give you a number, let's say it's around 0.9332. What does that mean? It means there's about a 93.32% chance that a randomly selected student scored less than 85 on that test. Pretty cool, huh?
But what if you want the probability of scoring greater than a certain number? Say, more than 90? Your Z-score for 90 might be 2.0. The Z-table will tell you the probability of scoring less than 2.0, which is about 0.9772. But we want greater than, remember?
No sweat! Since the whole area under the bell curve represents 100% (or 1 in probability terms), you just subtract the probability of scoring less than from 1. So, 1 - 0.9772 = 0.0228. That means there's only about a 2.28% chance of scoring more than 90. A rare bird, indeed!
And what about the probability of being between two scores? Let's say between 75 and 85. We already know the Z-score for 85 is 1.5 (probability of less than 0.9332). Now, let's find the Z-score for 75. If the mean is 70 and the standard deviation is 10, Z = (75 - 70) / 10 = 0.5. Looking up 0.50 in our Z-table, we get about 0.6915.
So, the probability of scoring less than 85 is 0.9332, and the probability of scoring less than 75 is 0.6915. To find the probability of being between them, we just subtract the smaller from the bigger: 0.9332 - 0.6915 = 0.2417. Voila! There's about a 24.17% chance of landing in that sweet spot.
It's all about using that Z-table as your trusty sidekick. You calculate the Z-score, look it up, and then do a little bit of simple subtraction or addition depending on whether you're looking for "less than," "greater than," or "between." Easy peasy, lemon squeezy!
So, why is this whole bell curve thing even a big deal?
Well, loads of real-world stuff follows this pattern. Think about the heights of adult males in a country. Most will be around the average, with fewer people being super tall or super short. Or the weights of apples in a harvest. Or even the lifespan of a particular type of light bulb!
This standard normal distribution is like a universal language for describing these kinds of natural variations. It helps us make predictions, understand risks, and basically make sense of the messy world around us. It’s pretty powerful, don't you think?
Let's Recap the Magic Steps:
1. Figure out your data point (X). This is the specific value you're interested in. Like that score of 85 we talked about.
2. Know the mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ). These are your distribution's superpowers. They tell you the center and spread of your data.
3. Calculate the Z-score. Remember the formula? Z = (X - μ) / σ. This is your ticket to the Z-table!

4. Use the Z-table. Look up your Z-score. Most tables give you the probability of being less than that score. It's your guide!
5. Adjust for "greater than" or "between." If you need the probability of being greater than, subtract the Z-table value from 1. If you need the probability of being between two scores, find the Z-scores for both, look them up, and subtract the smaller probability from the larger one.
And that's pretty much it! It sounds like a mouthful when you spell it all out, but when you're actually doing it, it flows. You get a question, you pull out your trusty calculator, you find your Z-score, and you peek at the Z-table. You're practically a statistics superhero!
Don't be shy if you get a weird number at first. Practice is key! The more you do it, the more natural it becomes. Think of it like learning to ride a bike. A few wobbles here and there, but soon you're cruising!
And if you ever get stuck, just remember the bell curve. It’s always there, a comforting, symmetrical presence. Most things cluster around the middle, and the further you get from the middle, the rarer things become. It's a fundamental truth of the universe, practically!

So, next time you see a problem involving probabilities and a normal distribution, don't panic. Just think of our coffee chat. Grab your Z-score, consult your Z-table, and you’ll be finding those indicated probabilities like a pro. You’ve got this!
Seriously, it’s not that complicated. Once you get the hang of the Z-score and how to read that table, you're golden. It’s like unlocking a secret level in a video game, but instead of points, you’re getting insights into the world. How cool is that?
And hey, if you’re working with a normal distribution that isn’t standard (meaning its mean isn’t 0 and its standard deviation isn’t 1), guess what? You just convert it to a standard normal distribution using that Z-score formula. It's the universal key, the Rosetta Stone of probability! You’re basically making any normal distribution play nice with the standard Z-table. Talk about versatile!
So, go forth and conquer those probability problems! You're armed with the standard normal distribution, the Z-score, and the mighty Z-table. What could possibly go wrong? (Okay, maybe don't answer that, but you get the idea!)
Just remember to double-check your calculations. A tiny mistake can lead to a wildly different probability. It's like baking – a pinch too much of this, and your cake might be a little... well, not perfect. But with a little care, you’ll be a probability baking master!
And that, my friend, is the lowdown on finding probabilities using the standard normal distribution. No more fear, just friendly understanding and a trusty Z-table. Let's grab another coffee and celebrate your newfound statistical prowess!
