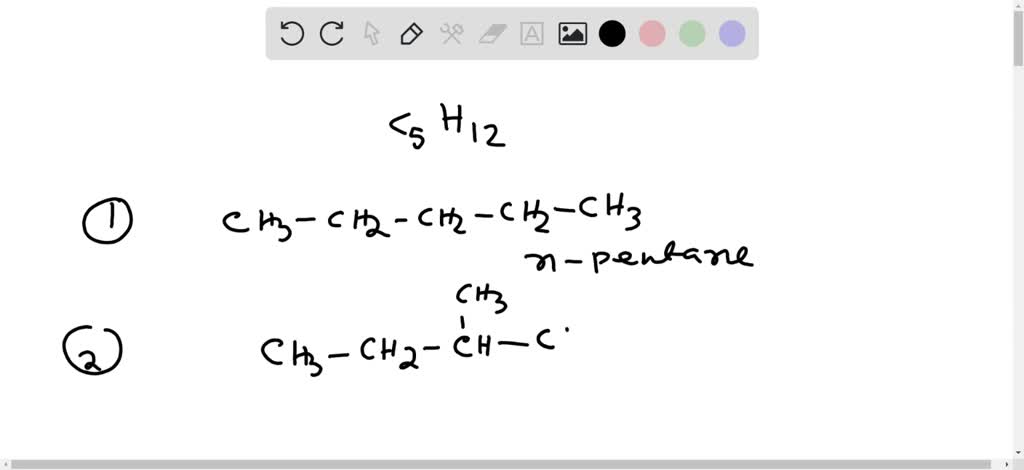
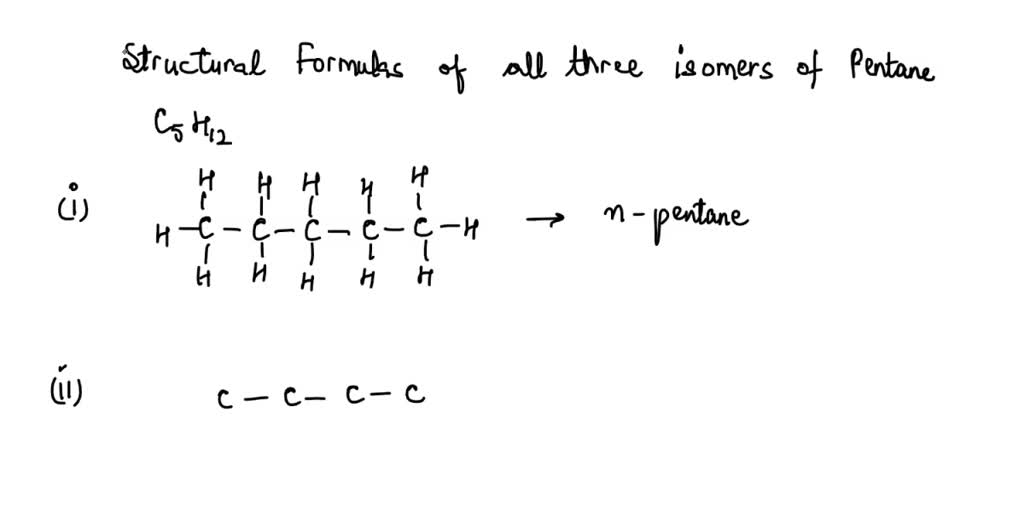
Draw The Structural Formulas For Three Isomers Of Pentane C5h12
..jpg)
Hey there, science enthusiasts and the wonderfully curious! Ever looked at a recipe and thought, "Wait, how can so many ingredients make something so different?" You know, like how butter, flour, sugar, and eggs can become a cake, cookies, or even a fluffy pancake? Well, get ready for a similar kind of delicious brain-food, but this time, it’s all about molecules and the magic of “isomerism.”
Today, we’re diving into the fascinating world of pentane, which has the chemical formula C5H12. Now, that might sound like a mouthful, but stick with me! Imagine you have a box of 5 LEGO bricks shaped like little cylinders (that’s our 5 carbon atoms, or ‘C’) and 12 tiny connector pins (those are our 12 hydrogen atoms, or ‘H’). You can snap these together in different ways, right? Even though you have the exact same number of bricks and pins, you can build some surprisingly different structures.
This is where “isomers” come in. Think of them as molecular siblings. They have the same set of “building blocks” – the same number and types of atoms – but they’re arranged in a slightly different order. This difference in arrangement can lead to some pretty neat variations in their properties, kind of like how a neatly stacked pile of pancakes is different from a fluffy, layered cake, even if they use mostly the same ingredients.
So, why should you, the everyday marvel that you are, care about isomers of pentane? Well, these little molecular variations are the unsung heroes behind a lot of things we encounter daily. From the fuels that power our cars to the plastics that make up our gadgets, understanding how atoms can be put together in different ways helps chemists create and improve all sorts of materials. It’s like understanding how to twist and shape dough differently to get a chewy bread versus a crispy cracker – it's all about the structure!
Meet the Pentane Family: Three Different Personalities!
Let’s get our hands (virtually speaking!) dirty and draw out these three isomers of C5H12. We’ll call them by their common names, which are pretty descriptive if you squint your chemical eyes.
1. The Straight-Laced One: n-Pentane
First up, we have the most straightforward member of the family. This one is called n-pentane. The ‘n’ stands for ‘normal,’ and boy, is it ever! Imagine a perfectly straight line of 5 carbon atoms linked together end-to-end. Then, we’ll attach all the hydrogen atoms to fill in the gaps.
Here’s a little visual for you. Think of it like a very orderly row of 5 houses on a street, all connected by their back fences:
C - C - C - C - C
Now, let’s add the hydrogens. Each carbon atom likes to have 4 bonds in total. So, the ones at the ends only need 3 hydrogens each, because they’re already bonded to one carbon. The ones in the middle are bonded to two carbons, so they need 2 hydrogens each.
(Imagine drawing this out: a line of 5 Cs, with 3 Hs on each end C, and 2 Hs on each of the three middle Cs. It looks like a long, skinny molecule!)
This straight, linear structure makes n-pentane pretty predictable. It’s a liquid at room temperature and is a component of gasoline. Think of it as the reliable workhorse of the pentane family – it gets the job done without any fuss.
2. The Branching Buddy: Isopentane (or 2-Methylbutane)
Next, we meet a bit of a rebel, or perhaps just someone who likes to mix things up. This isomer is called isopentane, or more formally, 2-methylbutane. Here, our 5 carbon atoms decide not to form one long chain. Instead, we have a main chain of 4 carbon atoms, and then one carbon atom branches off from the second carbon in the chain. It’s like one house on the street decided to build a little extension on its side, or a tree with a main trunk and a sturdy branch.
Let’s visualize this. We have our 4-carbon chain, and a single carbon hanging off the side:
C

|
C - C - C - C
Again, we fill in the hydrogens to make sure each carbon has 4 bonds. The carbon at the very tip of the branch will have 3 hydrogens. The carbon it’s attached to (the second one in the main chain) will have just one hydrogen because it’s bonded to three other carbons. The end carbons of the main chain will have 3 hydrogens each, and the middle carbon of the main chain will have 2 hydrogens.
(Picture this: a chain of 4 Cs, with one C sticking up from the second C. Count the Hs! It’s still 5 Cs and 12 Hs in total!)
This branching makes isopentane a bit different from its straight-laced cousin. It’s also a liquid and is used in fuels. The difference in shape can affect how easily the molecules pack together and how they behave, especially when it comes to burning. It’s like a slightly more agile dancer compared to the rigid march of n-pentane.
3. The Super-Branched One: Neopentane (or 2,2-Dimethylpropane)
Finally, we have the most compact and symmetrical member of the pentane club: neopentane, or 2,2-dimethylpropane. This one is really interesting! Here, we have a central carbon atom, and then four other carbon atoms are all attached directly to it, like the spokes on a wheel, or a central hub with four arms reaching out. It’s like one giant house with four identical apartments branching off its very core!
Here’s the drawing:
C
|
C - C - C
|
C
Wait, that only shows 3 Cs attached to the middle one. Let's try again to get all 5 carbons:
C
|
C - C - C
|
C
Ah, I made a mistake in my drawing explanation! Let's fix that and make it clear:
Imagine one carbon atom right in the center. Then, attach four other carbon atoms to that central one, one on each side (up, down, left, right). That gives us our 5 carbons!
C
|

C - C - C
|
C
No, that's still not right for neopentane! Neopentane has a central carbon bonded to four other carbons. Let’s draw it correctly this time:
C
|
C --- C --- C
|
C
Okay, I’m really struggling to draw this clearly with simple characters! Let’s try to describe it: You have a central carbon atom. Then, you have four other carbon atoms each attached to that central carbon. So, it looks like a plus sign (+) but with a carbon atom at each intersection.
Let's try a text representation that’s a bit better:
CH3
|
CH3 - C - CH3
|
CH3
See? A central carbon atom (the ‘C’) is bonded to four other carbon atoms. And each of those outer carbon atoms is bonded to 3 hydrogen atoms, because they are only bonded to that one central carbon. The central carbon is bonded to 4 other carbons, so it has no hydrogens attached. This gives us a very compact, almost spherical shape!
(Try to sketch this out! A carbon in the middle, with four arms, each ending in a carbon. Then, each of those outer carbons has 3 hydrogens.)
This super-branched structure gives neopentane unique properties. It’s also a liquid, but it has a different boiling point than the other two. Because it’s so symmetrical and rounded, the molecules don’t pack together as tightly, affecting how easily they flow and interact. It’s like a perfectly round bouncy ball compared to a long, thin rope – they’ll move and behave very differently!
Why Does This Matter to You?
You might be thinking, "Okay, cool drawings, but how does this affect my life?" Well, these tiny differences in molecular shape are a huge deal in chemistry and beyond!
For instance, in fuels, the branching of hydrocarbons (molecules made of carbon and hydrogen, like pentane) affects how smoothly they burn. This is measured by the "octane rating" of gasoline. Isomers that are more branched tend to burn more evenly and resist knocking in your engine. So, the next time you fill up your car, you're indirectly benefiting from chemists understanding these isomer differences!
It's also fundamental to the plastics, medicines, and materials we use every day. The precise way atoms are arranged can change a substance from being a harmless ingredient to something that causes an allergic reaction, or from a floppy plastic bag to a rigid container. It’s all about the 3D puzzle!
So, the next time you see a chemical formula like C5H12, remember it's not just a bunch of letters and numbers. It's a hint at a whole family of molecules, each with its own personality and purpose, all thanks to the incredible versatility of how atoms can be connected. It’s the universe’s way of showing us that even with the same basic ingredients, you can create a whole spectrum of amazing things!
