Determine The Following Indefinite Integral. Check Your Work By Differentiation
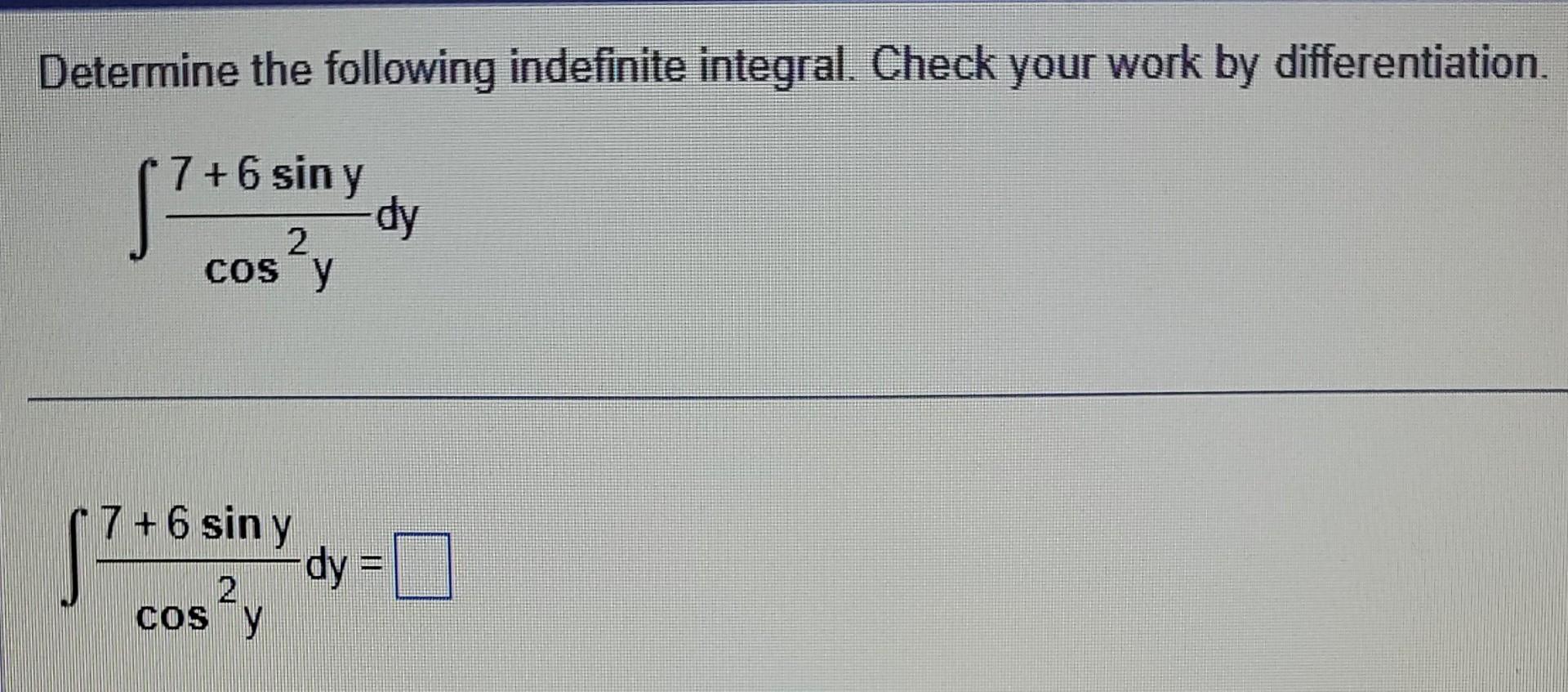
Ever feel like you're on a mathematical treasure hunt, trying to uncover a hidden original before things get complicated? Well, get ready for some fun, because today we're diving into the wonderfully rewarding world of indefinite integration! Forget dry formulas; think of this as a detective story where the clues are functions and the goal is to find the 'master function' that, when differentiated, leads you back to your clue. It's a core concept in calculus, and once you get the hang of it, it unlocks a whole universe of problem-solving possibilities, from calculating areas under curves to understanding motion and beyond. It’s a fundamental tool used by scientists, engineers, economists, and even artists to model and understand the world around them.
The Thrill of the Un-Derivative!
So, what exactly is this indefinite integral we're talking about? Imagine you're given a function, let's call it $f(x)$. Your mission, should you choose to accept it, is to find another function, let's call it $F(x)$, such that when you take the derivative of $F(x)$, you get back to our original $f(x)$. In mathematical terms, this is written as $\int f(x) \, dx = F(x) + C$. That mysterious '+ C' is a big deal, and we'll get to why it's so important in a moment. It represents any constant that could have been there because, remember, the derivative of any constant is zero!
The beauty of indefinite integration lies in its versatility. It's the inverse operation of differentiation. If differentiation is like breaking something down into its components, integration is like putting it back together. This makes it incredibly useful for solving a wide range of problems. For instance, if you know the rate at which something is changing (its derivative), you can use indefinite integration to find out the original amount or quantity. This is fundamental in physics for understanding velocity and position, in economics for analyzing costs and revenues, and in biology for tracking population growth. It's like having a rewind button for mathematical processes!
Think of it this way: If differentiation is like finding the slope of a mountain at any given point, indefinite integration is like finding the actual path of the mountain itself, given just its slope! And that little '+ C' is like acknowledging that there might be several different mountain paths that have the same general slope profile – they just start at different altitudes.
A Concrete Example: Let's Solve!
Let's get our hands dirty with a simple example. Suppose we want to determine the indefinite integral of $f(x) = 2x$. This means we're looking for a function $F(x)$ such that its derivative is $2x$. We know from our differentiation rules that the derivative of $x^2$ is $2x$. So, it seems like $F(x) = x^2$ might be our answer. But wait! What about the '+ C'? If we had $F(x) = x^2 + 5$, its derivative would still be $2x$. The same goes for $x^2 - 100$, or $x^2$ plus any constant. This is why we always add that constant of integration, denoted by '+ C', to our indefinite integral. It accounts for all the possible original functions.

So, the indefinite integral of $2x$ is $\int 2x \, dx = x^2 + C$. We've found our potential original function!
The Detective's Final Check: Differentiating to Confirm
Now for the fun part: checking our work! This is where the detective work really pays off. To make sure we've found the correct indefinite integral, we simply take the derivative of our answer. If we get back our original function, we've solved the case!
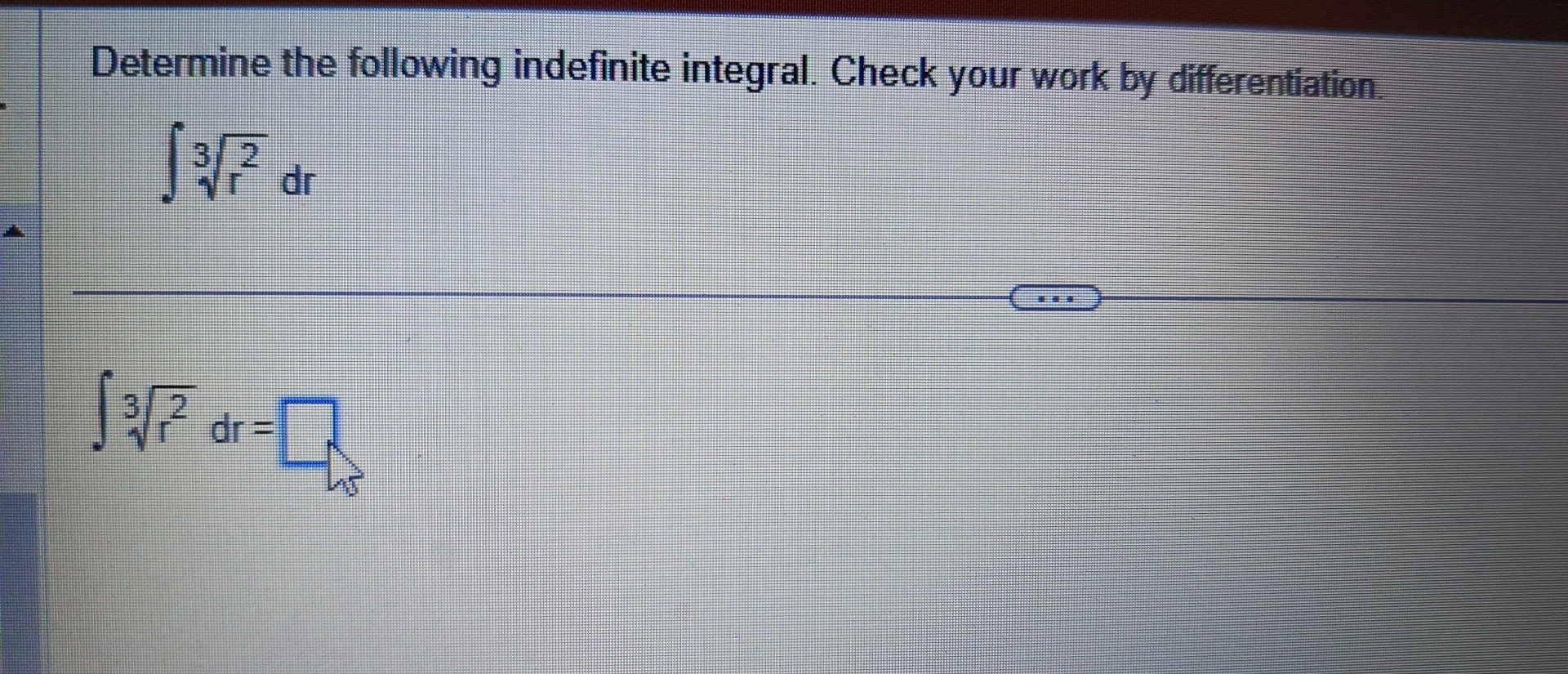
In our example, we found that $\int 2x \, dx = x^2 + C$. To check, we differentiate $F(x) = x^2 + C$. Taking the derivative of $x^2$ gives us $2x$. And the derivative of the constant $C$ is, as we know, $0$. So, the derivative of $x^2 + C$ is $2x + 0 = 2x$. Voilà! This is exactly our original function, $f(x) = 2x$. Our solution is confirmed, and we've successfully completed our mathematical treasure hunt!
This process of finding the indefinite integral and then checking it by differentiation is a fundamental skill in calculus. It's not just about getting the right answer; it's about building a deep understanding of the relationship between functions and their rates of change. So, the next time you encounter an indefinite integral, embrace the challenge, enjoy the process of discovery, and always remember to perform that satisfying final check!
