Convert Startfraction 3 Pi Over 8 Endfraction Radians To Degrees.

Alright, so imagine you're trying to explain something to your friend, but you're speaking two different languages. It’s kinda like that with angles, but instead of French and English, it’s radians and degrees. We're gonna tackle converting 3π/8 radians into degrees, and trust me, it's less complicated than trying to assemble IKEA furniture with a blurry instruction manual.
Think of radians like the fancy, scientific way of measuring angles. It's all about how far an arc stretches around a circle compared to its radius. Degrees, on the other hand, are like the comfortable, worn-in slippers of angle measurement. Everyone knows what 90 degrees is – that's a nice, square corner, like the edge of your TV. Or 180 degrees – that's a straight line, like your boss's mood after a Monday morning meeting.
So, why do we even bother with radians? Well, in math and physics, they make a lot of formulas just nicer. It’s like having a secret handshake that makes everything flow smoothly. But for us regular folks, degrees are usually our go-to. It’s like ordering a regular coffee versus a quad-shot, half-caf, soy latte with extra foam – sometimes you just want the familiar, right?
Our mission today is to take this little guy, 3π/8 radians, and translate him into the more common language of degrees. Don't let that "π" (pi) scare you. Think of it as the magical number that connects a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately 3.14. It’s everywhere, from pizza slices to the perfect curve of a Ferris wheel.
Let’s break it down. We know that a full circle is 360 degrees. And in radians, a full circle is 2π radians. This is our golden ticket, our Rosetta Stone for converting between these two systems. It's like knowing that one gallon of milk is the same as four quarts – just a different way of measuring the same thing.
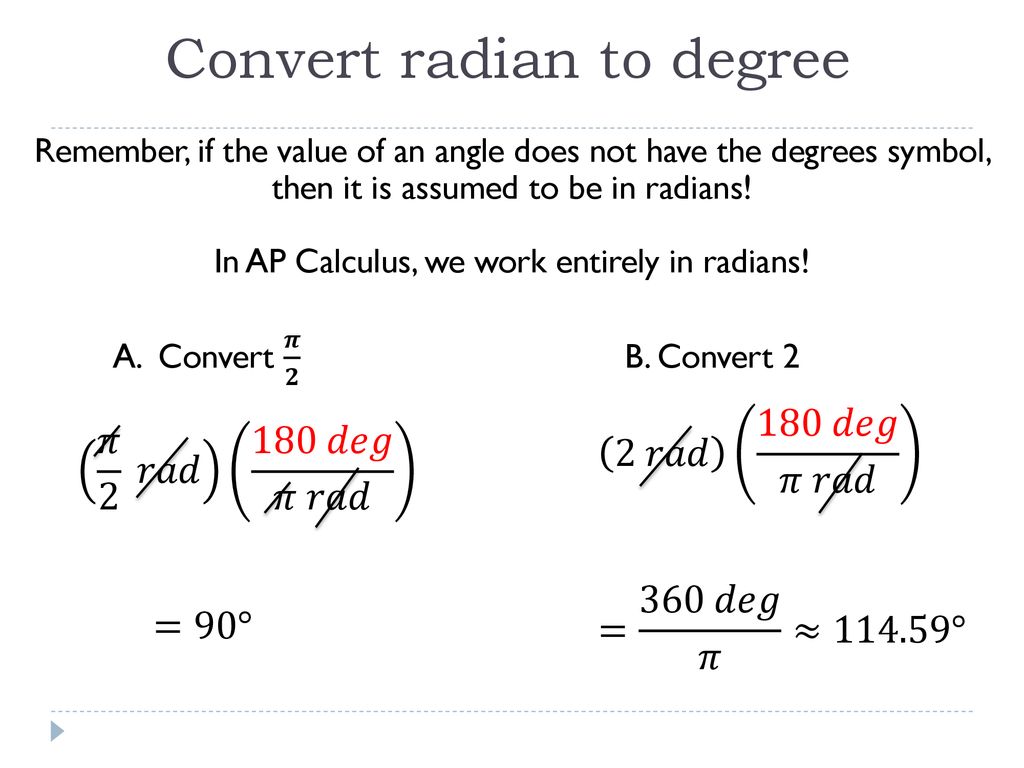
So, if 2π radians equals 360 degrees, then what does 1 radian equal in degrees? We can figure this out by dividing both sides of the equation by 2π. So, 1 radian = 360 degrees / 2π. Simplifying that, we get 1 radian = 180/π degrees. See? Pi is still there, but it’s chilling in the denominator, making things a bit more manageable.

Now, we have our conversion factor: 180/π degrees per radian. This is the magic spell we'll use to transform our 3π/8 radians. Think of it like having a recipe. You know how many cups of flour you need for one cake, so if you want to make half a cake, you just adjust the flour accordingly. Here, we want to convert 3π/8 radians, so we're going to multiply it by our conversion factor.
Here comes the fun part, the actual calculation! We take our angle in radians, which is 3π/8, and we multiply it by our conversion factor, 180/π. So it looks like this: (3π/8) * (180/π). Don't get flustered by all those symbols. It's like putting two puzzle pieces together. Notice anything cool? That "π" in the numerator and that "π" in the denominator are going to cancel each other out! Poof! Gone!
This is where the everyday analogies really shine. It’s like when you’re baking and you use both salt and baking soda, but in the end, you only taste the deliciousness of the cake. The pi’s were just tools to get us to our final flavor. Or think about it like ordering a pizza: you order one pizza (3π/8), and the price is listed in dollars (180/π). You multiply them to get the total cost.
So, after the pi’s do their vanishing act, we're left with (3/8) * 180. Now, this is a straightforward multiplication problem. It’s like saying, "I have 3 bags, and each bag has 8 apples. How many apples do I have?" Except here, we have 3 parts of something, and that something is worth 180 degrees. So we multiply 3 by 180.
3 multiplied by 180 is 540. Easy enough, right? Like counting your change after buying that coffee. So now we have 540, and it's still being divided by our 8 from the original fraction. So we have 540/8.
Now, we just need to perform that division. 540 divided by 8. You can do this in a few ways. You can punch it into a calculator, which is like using a GPS to get to your friend’s house. Or you can do it old-school with long division, which is like unfolding a giant paper map – a bit more effort, but satisfying when you get there.
Let's do the division. 540 divided by 8. 8 goes into 54 six times (6 * 8 = 48). We have 6 left over. Bring down the 0, and we have 60. 8 goes into 60 seven times (7 * 8 = 56). We have 4 left over. Since we're dealing with degrees, we can add a decimal and a zero. So we have 40. 8 goes into 40 five times (5 * 8 = 40). And we have zero left over. So, the answer is 67.5.

And there you have it! 3π/8 radians is equal to 67.5 degrees. Congratulations, you’ve just successfully navigated the sometimes-tricky waters of angle conversion. It’s like finally understanding a recipe that was written in a foreign language. You can now confidently tell someone that 3π/8 radians is the same as a nice, neat 67.5 degrees.
Think about where you might see this. That 67.5 degrees is a bit more than a right angle (90 degrees). It’s the kind of angle you might see in some architectural designs, or maybe the angle your phone screen is tilted back when you're casually scrolling. It's a perfectly reasonable, everyday kind of angle, even if it started out with that fancy "π" attached.
So, the next time you see an angle expressed in radians, don't feel intimidated. Just remember our little trick: multiply by 180/π, let those pi’s cancel out, and then do a bit of multiplication and division. It’s as straightforward as making a peanut butter and jelly sandwich, once you know the steps.
It's all about finding that common ground, that shared understanding. Radians and degrees are just different dialects of the same language. And by learning this conversion, you've become a bilingual angle expert! You can now switch between them like a seasoned diplomat, making sure everyone understands the precise angle of the situation.
So, to recap, we started with 3π/8 radians. We remembered that 180 degrees equals π radians (or 2π radians equals 360 degrees – same idea, just simplified). We multiplied our radian measure by the conversion factor (180/π). The π’s did a little dance and disappeared. We were left with (3/8) * 180. We crunched the numbers: 540 divided by 8. And voilà! 67.5 degrees.
It’s like converting currency. You have dollars, and you want to know how many Euros that is. You use an exchange rate. Our exchange rate here was 180/π degrees per radian. And just like you can’t buy a whole pizza with just half a dollar, you need to multiply the quantity of radians by the rate to get the equivalent in degrees.
So, go forth and convert! You’ve got the tools, you’ve got the knowledge. Whether you’re looking at a complex math problem or just trying to impress your friends with your newfound angle-converting prowess, you’re now equipped. Remember the pi’s canceling out – it’s the most satisfying part. Happy converting!
