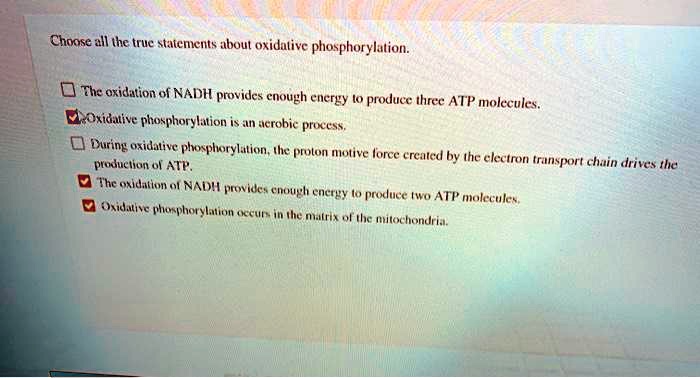
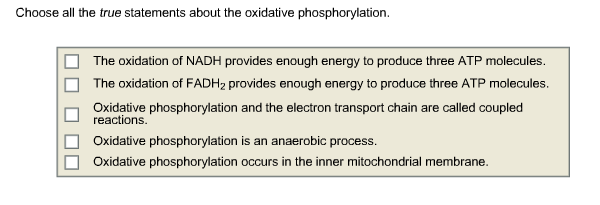
Choose All The True Statements About Oxidative Phosphorylation.

Alright, so imagine this: you're at a fancy café, sipping your latte, and suddenly your friend leans in, eyes wide, and whispers, "Okay, here's the deal. We need to pick out all the true statements about something called oxidative phosphorylation. It's basically the superhero origin story of our cells' energy, but way less capes and more… electrons. And it's a multiple-choice situation. Think of it like a pop quiz, but the prize is understanding why you can, you know, live."
So, what is this mythical beast, oxidative phosphorylation? Is it a new energy drink? A secret government project? Nope! It's the main event when it comes to making the energy currency of our cells, ATP. Think of ATP as the tiny, energetic coins that fuel everything your body does, from wiggling your toes to remembering that embarrassing thing you did in third grade. Without it, we'd be… well, we wouldn't be anything. So, let's dive into the juicy, slightly sweaty, world of making these energy coins, shall we?
The Electron Tango: A Grand Ball of Energy!
First off, let's talk about the main players. Oxidative phosphorylation is like a meticulously choreographed dance, and the dancers are a bunch of proteins shoved into the inner membrane of your mitochondria. Yeah, those tiny powerhouses within your cells that are so important, they basically get their own fan club. These proteins are the electron transport chain, and they're the rockstars of this energy concert.
So, what are they doing? They're like a cosmic game of hot potato, but instead of a potato, it's electrons. These electrons are coming from the food we eat – think of all those delicious carbs and fats you've been enjoying. They're carrying a bunch of energy, and the electron transport chain is designed to carefully and gradually strip that energy away. It’s like unwrapping a really, really complex present. You don’t just rip it open; you savour each layer.
As these electrons get passed from one protein to another, something super cool happens. They’re so full of energy that they start to push protons (think of them as tiny, positively charged hydrogen ions, like little energetic bouncy balls) from one side of the mitochondrial membrane to the other. This creates a gradient, which is basically just a fancy word for saying there are a TON more protons on one side than the other. Imagine trying to cram a million people into a tiny elevator – it creates a pressure, right? That’s kind of what’s happening here.
The ATP Synthase Maestro: Making the Magic Happen
Now, for the grand finale! This proton gradient is like a coiled spring, just waiting to be released. And who’s the conductor of this symphony? It’s a molecular machine called ATP synthase. This guy is an absolute legend. It's like a tiny, spinning turbine powered by the flow of those protons. As they rush back across the membrane, they make ATP synthase spin like crazy.
And here’s the mind-blowing part: with every rotation, ATP synthase grabs a bit of ADP (think of it as the “used” ATP coin) and a phosphate group and slams them together to make a fresh, shiny ATP coin. It’s literally building our energy currency out of spare parts, powered by the descent of protons. It’s so efficient, it’s almost cheeky. Like the universe saying, "Here, have some energy, you awesome biological organism."
This whole process is called oxidative phosphorylation because the oxidation of the electron carriers (taking electrons away) is coupled with the phosphorylation of ADP to make ATP. See? It all makes sense! Well, sort of. It's like saying "cake-making facilitated by flour-transfer and heat-application." Still sounds a bit technical, but you get the drift.
True Statements: The Moment of Truth!
Okay, so the café quiz is on! Let's see what’s actually true about this electrifying process. Prepare for some mind-bending facts that might just make you appreciate your mitochondria a little more.
Statement Selection Time! Choose Wisely, My Friends!
"The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane."
Is this true? You bet your energy-depleted socks it is! Imagine those mitochondria are like tiny cellular apartments, and the inner membrane is the fancy, high-security living room. That's where all the action happens. These protein complexes are like bouncers at an exclusive club, meticulously controlling the flow of electrons.
"Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain."

Absolutely! This is why we breathe oxygen. It’s the ultimate destination for those energetic electrons. Once they've done their thing, they need a place to chill, and oxygen is happy to oblige, forming water. So, in a way, we're constantly making tiny amounts of water with every breath. Talk about being hydrated from the inside out!
"The pumping of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane creates a concentration gradient."
Yep, that's the "pressure" we talked about! Think of it like filling up a water balloon. The more protons you cram in there, the more potential energy you store. This gradient is the engine that drives ATP synthesis. Without it, ATP synthase would just be… a really fancy, stationary piece of protein.
"ATP synthase utilizes the energy stored in the proton gradient to synthesize ATP."
This is the money shot! This is where the magic happens. The protons flow back through ATP synthase, like water through a dam, and bam – ATP is made. It’s a beautiful example of how nature harnesses energy in the most ingenious ways. It's like the universe's own tiny, cellular hydroelectric dam!
"This process directly uses glucose as a direct energy source."
Hold on a sec! Is this true? Nope, not directly. While glucose is the starting point for much of the energy that eventually fuels oxidative phosphorylation (through processes like glycolysis), glucose itself isn't just plopped into the electron transport chain. It gets broken down into smaller pieces, which then donate their electrons. So, it's more like glucose is the foundation for the energy-making building, not the building material itself.
"The majority of ATP produced by a cell is generated through oxidative phosphorylation."
You got it! While other methods of ATP production exist, oxidative phosphorylation is the heavyweight champion. It’s the most efficient way our cells can crank out ATP, especially when we're active. It's the difference between making a single-serving muffin and a giant, multi-tiered wedding cake. This is where the bulk of our cellular energy budget comes from.

"NADH and FADH2 are electron carriers that deliver electrons to the electron transport chain."
These guys are the delivery trucks of the electron world! NADH and FADH2 are like the Uber drivers, picking up electrons from the breakdown of food molecules and ferrying them over to the electron transport chain. Without them, those precious electrons wouldn't even get to the party. They're the unsung heroes, the backbone of this whole energy operation.
"This process occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell."
False alarm! Remember those fancy mitochondria? That's where the main event happens, specifically in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The cytoplasm is more like the waiting room, where some initial steps of energy extraction might occur, but the big ATP-making machinery is firmly within the mitochondrial walls. It's like trying to bake a cake in the living room – it just doesn't have the right equipment!
So, there you have it! Oxidative phosphorylation: a complex, amazing, and frankly, pretty vital process. It’s the reason you can keep reading this, keep sipping your latte, and generally keep being awesome. Next time you feel a burst of energy, give a little nod to your mitochondria. They’re working hard, one electron tango at a time.
