Carolina Exploring Mendelian Genetics For Ap Biology Answer Key
Hey there, future bio-buffs and curious minds! Ever wondered why your hair is curly while your best friend's is straight? Or why some peas are round and others are wrinkly? Well, get ready to dive into a world of tiny, invisible blueprints that dictate so much of what makes us, well, us! We're talking about the magical land of Mendelian Genetics, and trust me, it's way more exciting than it sounds.
Imagine a super-smart dude named Gregor Mendel, who lived way back when and apparently had a thing for pea plants. Like, a serious thing. He didn't have fancy microscopes or DNA sequencers, but this guy was a detective of the highest order, carefully observing how traits passed from one generation of peas to the next. He was basically the OG geneticist, and his work is the bedrock of everything we understand about how characteristics get passed down.
Mendel's big breakthrough was realizing that traits don't just magically blend. Instead, they're passed down in discrete little packages, which we now call genes. Think of them like tiny instruction manuals for different parts of an organism. Your eye color? That's a gene at work. Your ability to roll your tongue? Yep, another gene.
Now, here's where it gets really fun. For each gene, you usually get two copies – one from your mom and one from your dad. These copies are called alleles. So, for the "eye color" gene, you might have an allele for brown eyes and an allele for blue eyes. It's like getting two different flavors of the same ice cream!
But what happens when you have two different alleles? Does one win? Does it all get messy? Ah, this is where Mendel's genius truly shines! He figured out the concept of dominant and recessive alleles. A dominant allele is like the loudmouth at a party; it pretty much always makes its presence known. Even if you have one dominant allele and one recessive allele, the dominant trait will show up.

The recessive allele, on the other hand, is a bit more shy. It only gets a chance to express itself if you have two copies of it. So, if brown eye alleles are dominant over blue eye alleles, someone with one brown and one blue allele will have brown eyes. But to have blue eyes, you need to inherit two blue eye alleles. It's like a tiny genetic showdown happening inside you!
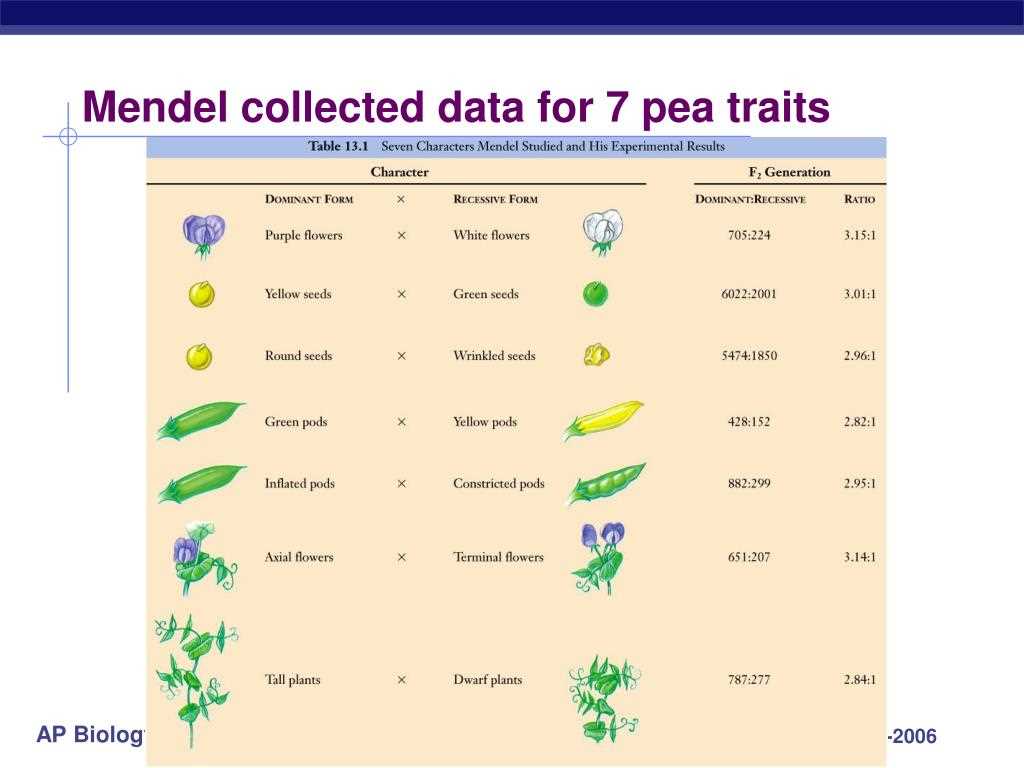
Let's put this to the test with Mendel's favorite subject: peas! Imagine a gene for pea color. Let's say the allele for yellow peas (Y) is dominant, and the allele for green peas (y) is recessive. If a pea plant inherits a Y and a y, it will be yellow. It needs two little 'y's to be green. So, if you see a patch of pea plants, the yellow ones could be a mix of "YY" (two yellow alleles) or "Yy" (one yellow, one green). The green ones, however, must be "yy." Sneaky, right?
Mendel didn't just stop at one trait. He was a trailblazer, and he also discovered the Law of Independent Assortment. This is where things get even more mind-bogglingly cool. It basically states that the alleles for different genes sort themselves out independently of each other. So, the gene for pea color doesn't care what the gene for pea shape is doing. They march to the beat of their own genetic drummer!

Think of it like this: when you get your genes from your parents, the gene for your hair color gets shuffled and dealt separately from the gene for your eye color. It’s not like all your brown-hair genes will end up with all your brown-eye genes. They get mixed and matched randomly, which is why you can have a person with brown hair and blue eyes, or blonde hair and brown eyes. It's a genetic cocktail!
This is also why siblings can look so different, even though they share pretty much the same parents. They're each getting a unique combination of alleles from Mom and Dad. It’s like they each opened a different grab bag of genetic goodies! This randomness is what creates all the amazing diversity we see in the world.
Now, let’s talk about how scientists and students figure all this out, especially when they're tackling those challenging AP Biology exams. This is where the trusty "AP Biology Answer Key" comes into play. It's not some magical cheat sheet, but rather a guide that helps you understand how to apply all these Mendelian principles. It breaks down complex problems into manageable steps, showing you how to use tools like Punnett Squares.

Oh, Punnett Squares! These are like little grids that help you visualize and predict the possible combinations of alleles an offspring can inherit. You set up one parent's alleles along the top and the other parent's alleles along the side, and then you fill in the boxes. It's a visual representation of those independent assortments and dominant/recessive interactions. It's like a genetic lottery ticket predictor!
For example, if you have a pea plant that's heterozygous for both color and shape (let's say YyRr, meaning it has alleles for yellow/green and round/wrinkled, with yellow and round being dominant), and you cross it with another YyRr plant, the Punnett Square will show you all 16 possible combinations of offspring. You can then figure out the probability of getting, say, a yellow, round pea versus a green, wrinkled one. It's pure genetic forecasting!
The AP Biology answer key is there to show you the logic behind solving these problems. It’s not about memorizing answers, but about understanding the process. It demonstrates how to identify genotypes (the actual allele combinations, like YY or Yy) and phenotypes (the observable traits, like yellow or green peas). It emphasizes the importance of clearly defining your alleles and understanding the parent genotypes.
It's also crucial to remember that while Mendel's work is foundational, genetics is a vast and complex field. There are things like incomplete dominance (where neither allele is fully dominant, leading to a blended trait, like pink flowers from red and white parents) and codominance (where both alleles show up fully, like blood types A and B). The AP Biology answer key often touches on these extensions to the basic Mendelian principles.
But don't let the extra bits overwhelm you! The core of Mendelian genetics, as laid out by our pal Gregor, is about understanding these fundamental rules of inheritance. It’s about recognizing that traits are passed down in predictable ways, driven by dominant and recessive alleles, and that different genes shuffle and sort independently. It’s a beautiful, orderly system at the heart of so much biological chaos (in the best way possible!).
So, when you're wrestling with those genetics problems for AP Biology, remember Gregor Mendel and his peas. Visualize those alleles, draw out your Punnett Squares, and trust in the process. The "answer key" is simply your guide to unlocking the secrets of these tiny genetic blueprints. It’s about seeing the patterns, understanding the probabilities, and appreciating the incredible way life perpetuates itself, one gene at a time. You’ve got this! Embrace the awesome power of your own genetic inheritance!
