Can I Contribute To Traditional Ira And Sep
Let’s talk about a topic that might sound a little dry at first, but trust us, it’s a real gem for anyone looking to boost their retirement savings with a bit of strategic flair! We’re diving into the fascinating world of retirement accounts, specifically the question that pops up for many self-employed individuals and small business owners: "Can I Contribute to a Traditional IRA and a SEP IRA?" It’s a question that unlocks a potential super-power for your financial future, and understanding the nuances can make a big difference in how much you squirrel away for those golden years. Think of it as unlocking a secret level in the game of retirement planning!
The "Why" Behind the Question
This question is popular because it speaks to a growing segment of the workforce: freelancers, solopreneurs, and small business owners. These go-getters are building their own dreams, and they deserve powerful tools to secure their own futures. Many have already heard about the benefits of a Traditional IRA – that trusty, tax-deferred account that’s been a retirement staple for decades. But then, they discover the magic of a SEP IRA (Simplified Employee Pension IRA), which often boasts higher contribution limits, making it incredibly attractive for those with higher incomes. The natural next step is to wonder if they can have their cake and eat it too, or rather, contribute to both to maximize their retirement nest egg.
Understanding the Players: Traditional IRA vs. SEP IRA
Before we answer the big question, let’s quickly get acquainted with our contenders:
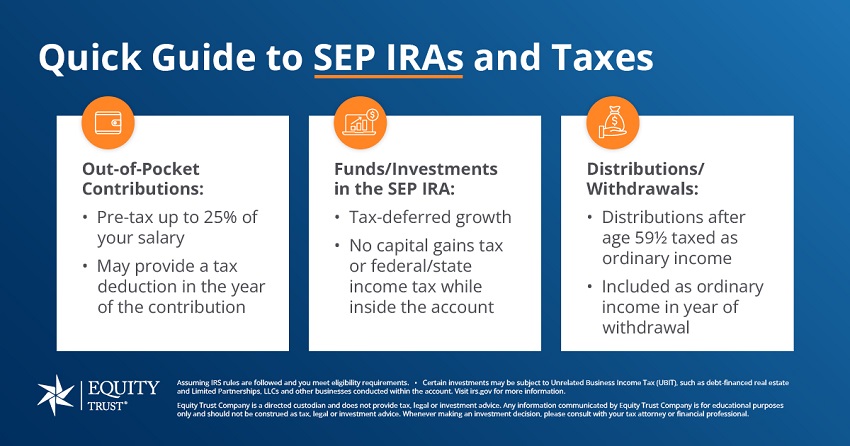
- Traditional IRA: This is your classic retirement savings account. You contribute pre-tax dollars (usually, though there are non-deductible contributions), and your money grows tax-deferred. You’ll pay ordinary income tax on withdrawals in retirement. The annual contribution limit is set by the IRS and changes periodically. For 2023, it was $6,500, with an additional $1,000 catch-up contribution for those aged 50 and over.
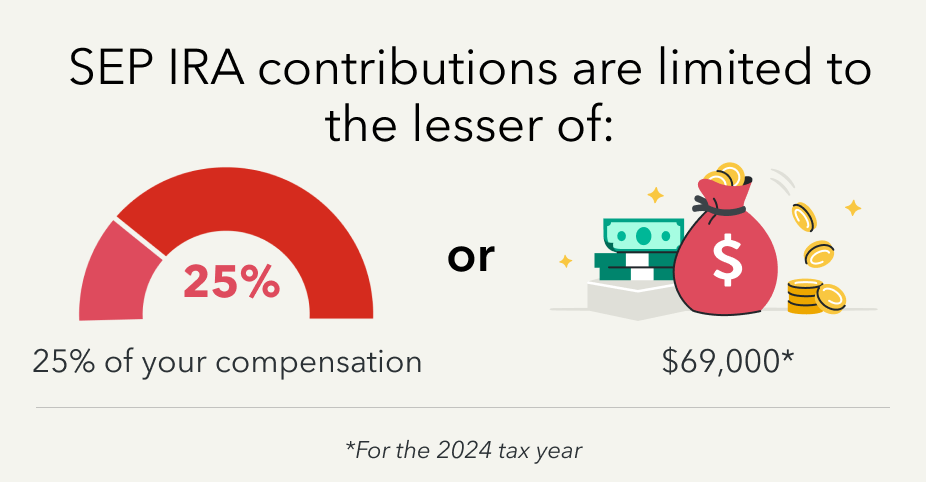
- SEP IRA: This is a retirement plan designed for self-employed individuals and small business owners. It’s funded entirely by the employer (which, if you’re self-employed, is you!). The contribution limits are significantly higher than for a Traditional IRA, based on a percentage of your net adjusted self-employment income, up to a substantial annual maximum. For 2023, the limit was the lesser of 25% of compensation or $66,000. Contributions are tax-deductible, lowering your current taxable income.
The Verdict: Can You Contribute to Both?
Now for the exciting part! The answer is a resounding yes, but with important distinctions.
Here’s the key: a SEP IRA is an employer-sponsored retirement plan. If you are self-employed and establish a SEP IRA for yourself, you are considered both the employer and the employee. When you contribute to a SEP IRA, you are making contributions in your capacity as the employer. Therefore, the contributions you make to your SEP IRA do not count towards the contribution limits of a Traditional IRA, where you are acting in your capacity as an individual. This means you can contribute to both accounts independently, leveraging the benefits of each.

Think of it this way: your SEP IRA contributions are for your business’s retirement plan, and your Traditional IRA contributions are for your personal retirement savings. They operate on different tracks!
Maximizing Your Savings Potential
The ability to contribute to both a Traditional IRA and a SEP IRA opens up a fantastic opportunity for strategic retirement planning. Here’s how you can leverage this:
Benefit 1: Higher Overall Contribution Limits. The most obvious advantage is the ability to save significantly more for retirement. You can max out your Traditional IRA contributions (subject to income limitations for deductibility if you also have a workplace retirement plan, though this is less of a concern with a SEP IRA as it's your own plan) and then contribute a substantial amount to your SEP IRA, up to the IRS limits. This is especially powerful for those with higher self-employment income.
Benefit 2: Diversified Tax Advantages. Traditional IRA contributions offer tax deferral, while SEP IRA contributions provide an immediate tax deduction. By contributing to both, you can strategically manage your current tax burden while building a robust tax-deferred or tax-advantaged retirement portfolio.

Benefit 3: Flexibility for Different Income Levels. If your income fluctuates, the SEP IRA’s flexibility allows you to adjust contributions year by year based on your profitability. You can still contribute to your Traditional IRA consistently, ensuring you’re always moving forward with your personal savings goals.
Important Considerations
While the answer is generally "yes," there are a few nuances to keep in mind:
- Deductibility of Traditional IRA Contributions: If you are covered by a retirement plan at another job (unlikely if you are solely self-employed and establishing your own SEP), or if your income is above certain thresholds, your ability to deduct Traditional IRA contributions might be limited. However, even if non-deductible, the earnings grow tax-deferred.
- Timing of Contributions: SEP IRA contributions can typically be made until the tax filing deadline of your business (including extensions), giving you extra time to decide how much to contribute based on your annual income. Traditional IRA contributions are generally due by the tax filing deadline (April 15th of the following year for the previous year’s contributions), with an extension available.
- Understanding Your Business Structure: The rules can be slightly different depending on whether you are a sole proprietor, partner, or corporation. It’s always wise to consult with a tax professional to ensure you’re setting up and contributing to your accounts correctly.
So, the next time you’re thinking about retirement savings and you’re a self-employed whiz, remember this dynamic duo: Traditional IRA and SEP IRA. They aren’t mutually exclusive; they’re a powerful tag team ready to help you build a brighter financial future. It’s not just about saving; it’s about saving smart and taking advantage of every opportunity the tax code offers!
