Art-labeling Activity Overview Of The Cardiac Conduction System
Ever thought about what’s really going on inside your chest when you feel that little flutter of excitement, or the comforting thump-thump of your own heartbeat? It’s not just random noise, you know. It’s a finely tuned orchestra, a tiny, relentless superhero team working around the clock to keep you alive and kicking. And at the heart of this incredible operation is something called the Cardiac Conduction System. Now, that might sound like something straight out of a sci-fi movie, but trust me, it’s way cooler and way more down-to-earth than you’d think.
Imagine your heart as a bustling city. This city has its own traffic control system, its own power grid, and its own set of rules for how things get done. The Cardiac Conduction System is basically that city’s internal communication network, whispering instructions to every single cell to get them to do their job in perfect sync. Without it, your heart would be like a band where everyone’s playing a different song at a different speed – utter chaos!
Think of it as the heart's very own DJ, dropping the beat and making sure everything flows smoothly.
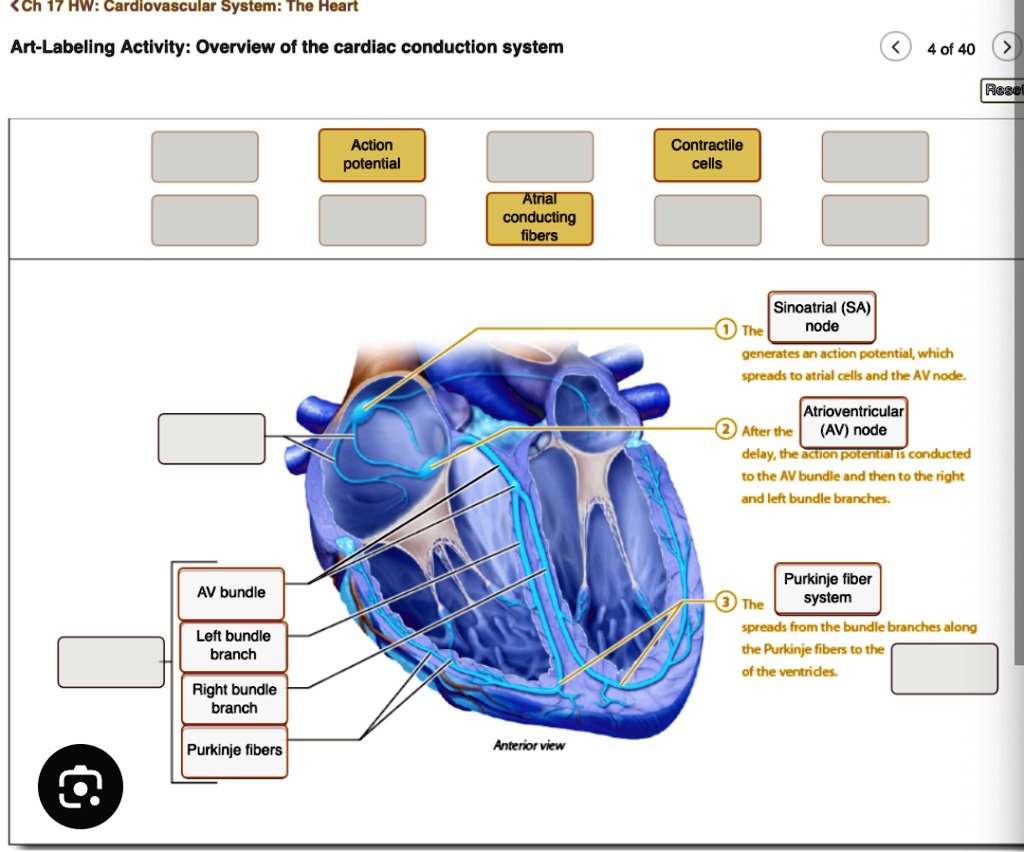
So, how does this magical system work? Let’s meet the main players, shall we? First up, we have the Sinoatrial (SA) node. This little guy is the undisputed boss, the pacemaker. It’s located in the upper right chamber of your heart, and it’s the one that sends out the initial electrical signal. It’s like the spark plug that gets the whole engine going. What’s fascinating about the SA node is that it’s not a rigid, unfeeling piece of tissue. It’s actually made of specialized cells that can generate their own electrical impulses. They’re like tiny, self-powered batteries, constantly firing off signals without needing any outside prompting. Pretty neat, right? It’s this spontaneous generation of electricity that makes it the natural pacemaker.
Once the SA node gets its groove on, the signal doesn't just sit there. Oh no, it travels! It moves through the walls of the heart's upper chambers, the atria, telling them, “Okay, everyone, it’s time to squeeze!” This squeezing action pushes blood down into the lower chambers, the ventricles. It's a coordinated effort, a perfectly choreographed dance of contraction. You can almost picture the atrial cells getting the message and then passing it along, like a whispered secret spreading through a crowd.
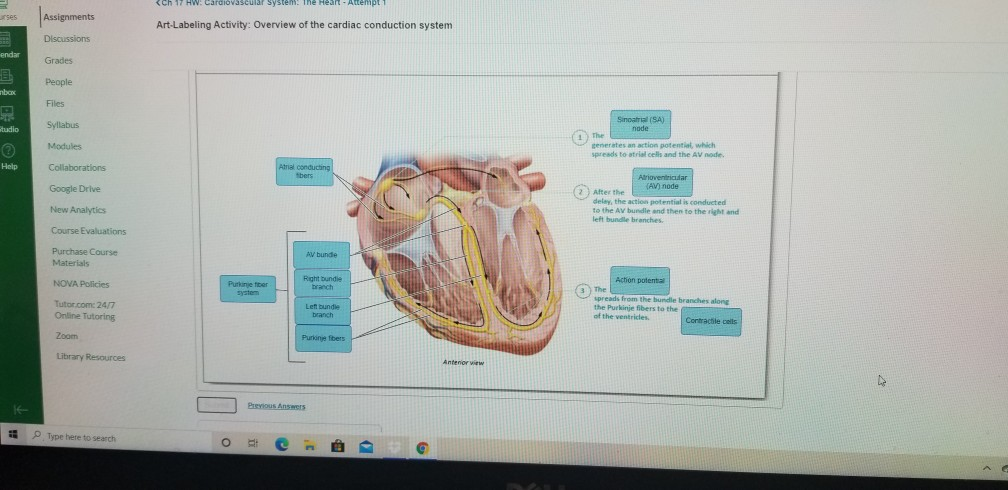
But here’s where it gets even more interesting. The signal can’t just rush straight into the ventricles. There’s a brief pause, a moment of reflection, at a special junction called the Atrioventricular (AV) node. This AV node is like the helpful, but slightly cautious, administrator. It’s the gatekeeper, ensuring that the atria have fully emptied their blood before the ventricles are given the green light to contract. This pause is crucial. Without it, the ventricles might try to squeeze before they're ready, leading to a less efficient pumping action. It’s a small delay, but it makes a huge difference. Think of it as the conductor pausing for dramatic effect before the main crescendo.
After its little pit stop at the AV node, the electrical signal gets a turbo boost. It heads down through a pathway called the Bundle of His, which then splits into the bundle branches. These branches are like the superhighways of the heart’s electrical system, carrying the signal rapidly down into the ventricles. They're designed for speed and efficiency, making sure that both ventricles get the message at the same time, so they can contract together in a powerful, unified squeeze. This synchronized contraction is what pushes blood out to the rest of your body and to your lungs. It’s the big, booming finale of the heart’s performance.
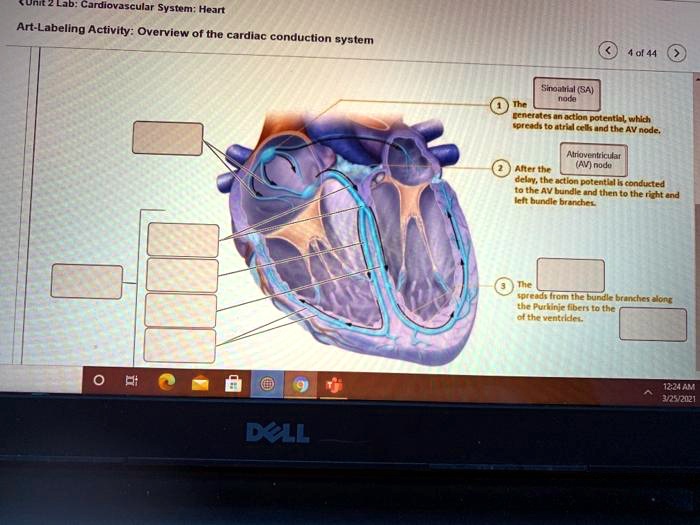
Finally, the signal reaches the very tips of the ventricles, spreading out through a network of tiny fibers called Purkinje fibers. These fibers are like the enthusiastic fans at the back of the stadium, making sure the message reaches every single corner. They ensure that the entire ventricular muscle contracts evenly and powerfully, giving you that strong pulse you can feel in your wrist or neck. It’s the final flourish, the grand send-off for the blood on its journey.
What’s truly heartwarming is that this entire intricate process happens thousands of times a day, every single day of your life, without you having to think about it. It’s a testament to the body’s incredible engineering and its unwavering commitment to keeping us going. So next time you feel your heart beat, remember the amazing team working behind the scenes: the self-starting SA node, the thoughtful AV node, the speedy bundle branches, and the enthusiastic Purkinje fibers, all playing their part in the most important rhythm of your life.
