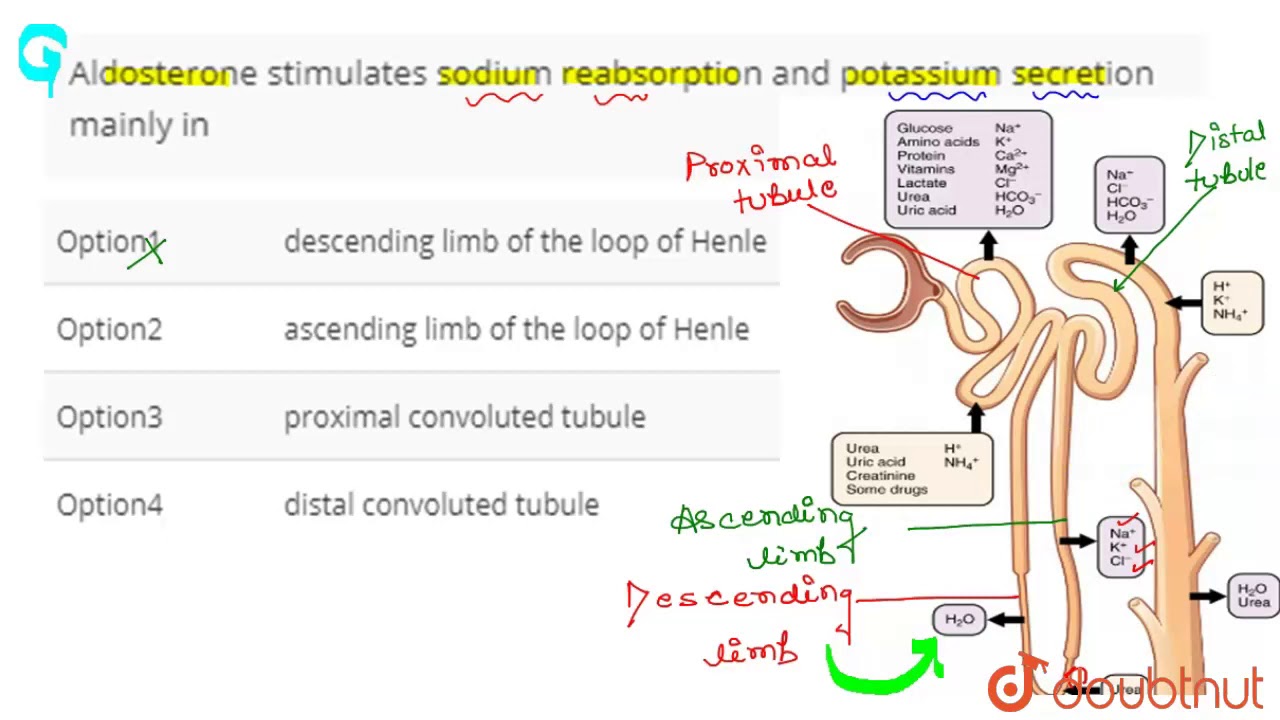
Aldosterone Stimulates Sodium Reabsorption And Potassium Secretion In
Hey there, health curious folks! Ever wonder what’s going on behind the scenes in your body, keeping everything running smoothly? It’s like a tiny, super-efficient city inside you, with all sorts of little workers doing their jobs. Today, we’re going to zoom in on one of these amazing workers, a hormone called aldosterone. You might have heard of it, or maybe it’s a brand new name, but trust me, it’s doing some seriously cool stuff to keep your body balanced.
So, what exactly is aldosterone up to? Think of it as a super-tuned balance keeper. Its main gig involves two very important minerals: sodium and potassium. These guys are everywhere in our bodies, and their levels need to be just right. Too much of one, or too little of another, and things can get a bit wobbly.
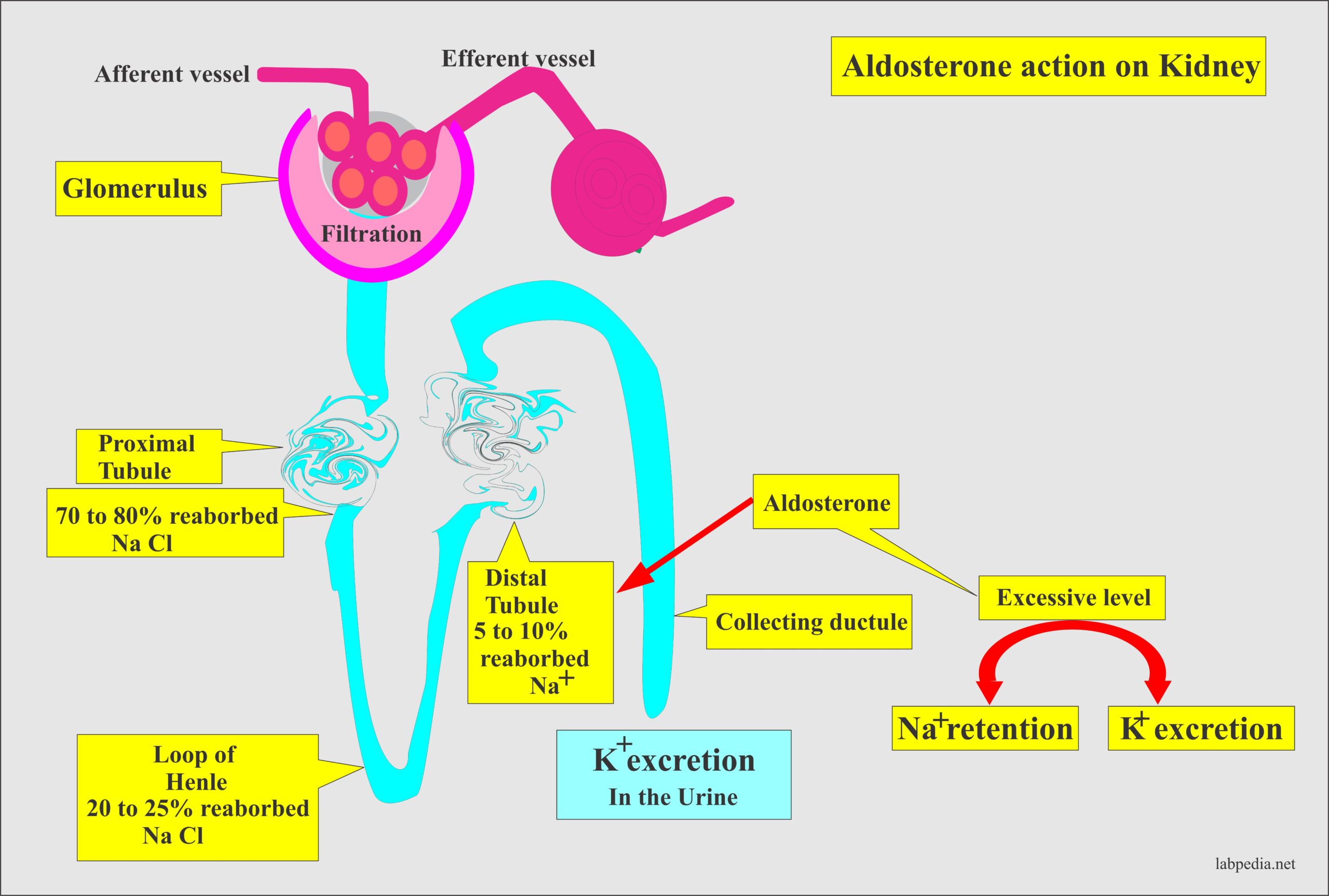
Aldosterone's primary superpower is its ability to tell your kidneys to do something pretty darn important: reabsorb sodium. Now, why is that a big deal? Well, sodium is a bit like the body’s water magnet. When sodium hangs out in your bloodstream, it pulls water along with it. This is crucial for maintaining your blood pressure and ensuring that your cells have enough fluid to function properly. Imagine a desert caravan; sodium is like the oasis, attracting the precious water the travelers desperately need.
So, when aldosterone shows up, it’s like giving your kidneys a gentle nudge, saying, "Hey, let’s hold onto this sodium, and by extension, this water!" This is especially important when your body might be losing fluid, like if you’ve been sweating a lot or haven’t had enough to drink. Aldosterone steps in to prevent you from becoming dehydrated and to keep your blood pressure from dropping too low. It’s like a wise old caretaker making sure there’s enough water in the garden.
But aldosterone isn’t just a one-trick pony. While it’s busy hoarding sodium, it’s also doing something else on the flip side: prompting your kidneys to secrete potassium. Potassium, on the other hand, is a bit of a different story. It’s super important for things like muscle contractions (yes, including your heart muscle!) and nerve signals. However, just like sodium, having too much potassium floating around can be problematic.
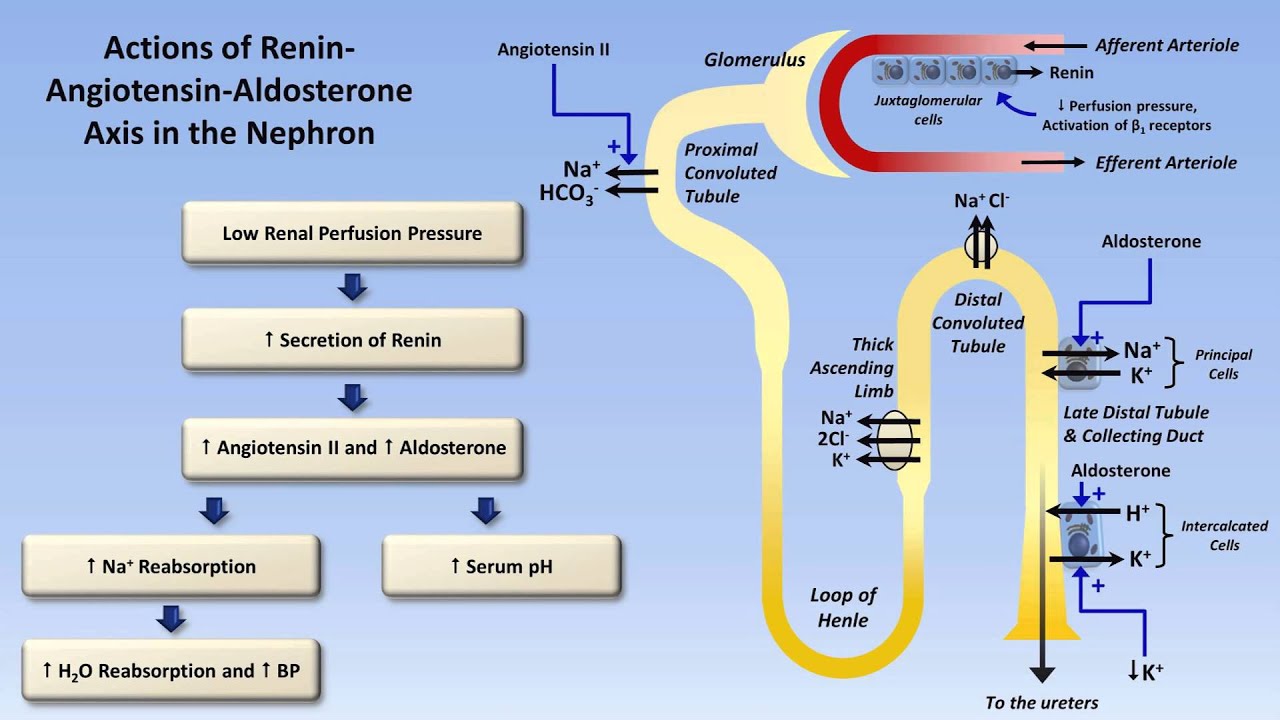
Think of your kidneys as the ultimate filtration system. They’re constantly sifting through your blood, deciding what to keep and what to get rid of. Aldosterone is like the supervisor of this process. It tells the kidney cells, "Okay, we need more sodium back in the system, so let's grab it from the filtrate. And while we’re at it, let’s push out some of this excess potassium into the urine.” It’s a clever way to maintain a healthy balance. You can imagine it like a chef carefully adjusting seasonings – a pinch of salt here, a dash of pepper there – to get the perfect flavor.
Why is this Sodium-Potassium Tango So Important?
This whole sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion dance is absolutely vital for our survival. It’s a key player in regulating your electrolyte balance. Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electric charge when dissolved in bodily fluids, and they’re essential for countless bodily functions. They’re the tiny sparks that keep the electrical signals in your body firing correctly.

Maintaining the right sodium-to-potassium ratio is like keeping your phone battery at an optimal level. If it’s too low, nothing works. If it’s too high, you can have problems too. Aldosterone ensures that this balance is maintained, which directly impacts your:
- Blood Pressure: As we mentioned, sodium helps regulate fluid volume, which is a major determinant of blood pressure. Aldosterone’s role in sodium reabsorption helps prevent your blood pressure from dipping too low.
- Heart Function: Potassium is critical for the electrical activity of your heart. Too much or too little can lead to irregular heartbeats. Aldosterone helps keep potassium levels in check.
- Nerve and Muscle Function: Those electrical signals we talked about? They rely on the right balance of sodium and potassium to travel along nerves and make muscles contract.
It’s like a symphony orchestra. You need all the instruments playing in harmony, and the right notes at the right time. Sodium and potassium are two of the most important instruments, and aldosterone is the conductor, making sure they’re in sync.
When Things Go Off-Balance
What happens when this system isn't working as it should? Well, if aldosterone levels are too high, you might find yourself holding onto too much sodium and water, leading to increased blood pressure. This is sometimes seen in conditions like hyperaldosteronism. On the other hand, if aldosterone levels are too low, you might lose too much sodium and water, and your body might struggle to get rid of excess potassium, which can be dangerous.
Think of a leaky faucet versus a blocked drain. Both cause problems, just in different ways. The body has intricate feedback loops to regulate aldosterone production. When your blood pressure drops or your body detects low sodium, signals are sent to produce more aldosterone. Conversely, when these levels are good, production is dialed back.
It’s fascinating, isn’t it? This one little hormone, working away in the background, has such a massive impact on your overall well-being. It’s a perfect example of the incredible complexity and elegance of the human body. So, the next time you’re enjoying a glass of water or feeling your heart beat steadily, you can give a silent nod to aldosterone and its tireless work keeping your sodium and potassium in perfect harmony!
