Albinism Is An Autosomal Recessive Condition. Which Circle Graph
Ever wondered about the amazing variety of traits we humans have? Some of us have curly hair, some straight, some blue eyes, and some brown. Today, we're going to explore a fascinating aspect of human genetics: albinism. While it might sound like a complex scientific term, understanding it can actually be quite fun and incredibly useful, especially when we think about how traits are passed down through families. It's a bit like a fascinating puzzle, and learning about it helps us appreciate the diversity that makes our world so interesting!
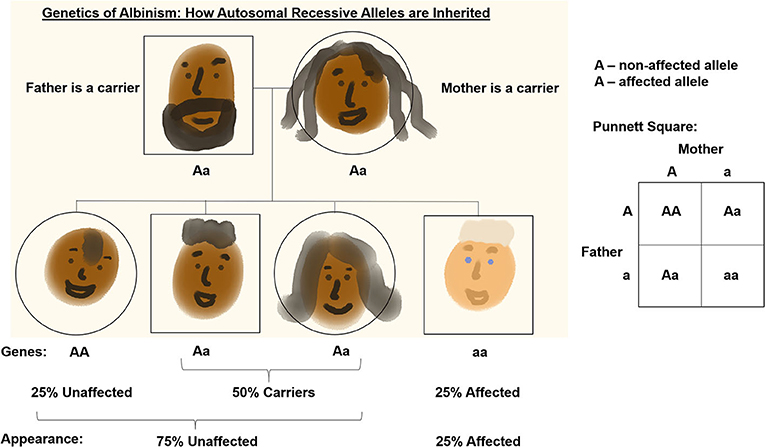
So, what exactly is albinism and why is it considered an autosomal recessive condition? Simply put, it means that to have albinism, a person needs to inherit a specific gene for it from both of their parents. Think of it like this: everyone has two copies of most of their genes. If one copy is the "standard" version and the other is the "albinism" version, a person usually won't have albinism. They'll be a carrier, meaning they have the gene but don't show the trait. However, if they happen to have children with another carrier, there's a chance (a 25% chance, to be exact!) that their child will inherit the "albinism" version from both parents, and thus have albinism.
Why is this knowledge so valuable? For beginners in genetics, it’s a fantastic introduction to the fundamental concepts of inheritance. It shows that traits aren't just random; they follow predictable patterns. For families who might have a history of albinism or are curious about genetic possibilities, understanding autosomal recessive inheritance can offer clarity and empower them with information. And for hobbyists interested in genealogy or even just appreciating the intricacies of life, it's another layer of wonder to discover. Imagine a circle graph illustrating this! You could have segments showing the probabilities: 25% chance of having a child with albinism, 50% chance of having a carrier child, and 25% chance of having a child with two "standard" genes. It’s a visual way to see the math behind nature!
The most visible trait associated with albinism is a lack of pigment, leading to very pale skin, light-colored hair (often white or very light blonde), and light eyes (often pink or blue). However, there are different types of albinism, and the degree of pigment difference can vary. This is a great example of variations within a condition! It’s not a one-size-fits-all situation. Some people might have more pigment than others.

Getting started with understanding this is super easy. You don't need a fancy lab coat! Simply start by talking to family members about inherited traits. Are there any unusual hair or eye colors in your family? Do people have conditions where they are sensitive to the sun? These kinds of conversations can spark curiosity. You can also look up simple, diagrammed explanations of autosomal recessive inheritance online – the circle graph idea is very common in these explanations. The key is to approach it with an open and curious mind, treating it like learning about a new hobby.
In conclusion, learning about albinism as an autosomal recessive condition is a truly rewarding experience. It demystifies a fascinating aspect of human genetics, offers valuable insights for families, and adds a layer of appreciation for the incredible diversity of life. It’s a journey of discovery that’s both educational and genuinely enjoyable!
